1Z0-051 Exam
Oracle 1Z0-051 Free Practice Questions 2021

1z0 051 dumps pdf are updated and 1z0 051 dumps are verified by experts. Once you have completely prepared with our 1z0 051 dumps pdf you will be ready for the real 1Z0-051 exam without a problem. We have 1z0 051 practice test. PASSED 1z0 051 pdf First attempt! Here What I Did.
Also have 1Z0-051 free dumps questions for you:
NEW QUESTION 1
Which two statements are true about constraints? (Choose two.)
- A. The UNIQUE constraint does not permit a null value for the colum
- B. A UNIQUE index gets created for columns with PRIMARY KEY and UNIQUE constraint
- C. The PRIMARY KEY and FOREIGN KEY constraints create a UNIQUE inde
- D. The NOT NULL constraint ensures that null values are not permitted for the colum
Answer: BD
Explanation:
B: A unique constraint can contain null values because null values cannot be compared to anything.
D: The NOT NULL constraint ensure that null value are not permitted for the column
Incorrect Answer: Astatement is not true Cstatement is not true
Refer: Introduction to Oracle9i: SQL, Oracle University Study Guide, 10-9
NEW QUESTION 2
SLS is a private synonym for the SH.SALES table.
The user SH issues the following command:
DROP SYNONYM sls;
Which statement is true regarding the above SQL statement?
- A. Only the synonym would be droppe
- B. The synonym would be dropped and the corresponding table would become invali
- C. The synonym would be dropped and the packages referring to the synonym would be droppe
- D. The synonym would be dropped and any PUBLIC synonym with the same name becomes invali
Answer: A
Explanation:
A synonym is an alias for a table (or a view). Users can execute SQL statements against the synonym, and the database will map them into statements against the object to which the synonym points.
Private synonyms are schema objects. Either they must be in your own schema, or they must be qualified with the schema name. Public synonyms exist independently of a schema. A public synonym can be referred to by any user to whom permission has been granted to see it without the need to qualify it with a schema name.
Private synonyms must be a unique name within their schema. Public synonyms can have the same name as schema objects. When executing statements that address objects without a schema qualifier, Oracle will first look for the object in the local schema, and only if it cannot be found will it look for a public synonym.
NEW QUESTION 3
Where can sub queries be used? (Choose all that apply)
- A. field names in the SELECT statement
- B. the FROM clause in the SELECT statement
- C. the HAVING clause in the SELECT statement
- D. the GROUP BY clause in the SELECT statement
- E. the WHERE clause in only the SELECT statement
- F. the WHERE clause in SELECT as well as all DML statements
Answer: ABCF
Explanation:
SUBQUERIES can be used in the SELECT list and in the FROM, WHERE, and HAVING
clauses of a query.
A subquery can have any of the usual clauses for selection and projection. The following
are required clauses:
A SELECT list
A FROM clause
The following are optional clauses: WHERE GROUP BY HAVING
The subquery (or subqueries) within a statement must be executed before the parent query that calls it, in order that the results of the subquery can be passed to the parent.
NEW QUESTION 4
Which four are types of functions available in SQL? (Choose 4)
- A. string
- B. character
- C. integer
- D. calendar
- E. numeric
- F. translation
- G. date
- H. conversion
Answer: BEGH
Explanation: Explanation: SQL have character, numeric, date, conversion function.
Incorrect Answer:
ASQL have character, numeric, date, conversion function.
CSQL have character, numeric, date, conversion function.
DSQL have character, numeric, date, conversion function.
FSQL have character, numeric, date, conversion function.
Refer: Introduction to Oracle9i: SQL, Oracle University Study Guide, 3-3
NEW QUESTION 5
You need to calculate the number of days from 1st January 2007 till date . Dates are stored in the default format of dd-mon-rr. Which two SQL statements would give the required output? (Choose two.)
- A. SELECT SYSDATE - '01-JAN-2007' FROM DUAL:
- B. SELECT SYSDATE - TOJDATE(X)1/JANUARY/2007") FROM DUAL:
- C. SELECT SYSDATE - TOJDATE('01-JANUARY-2007') FROM DUAL:
- D. SELECT TO_CHAR(SYSDAT
- E. 'DD-MON-YYYY') - '01-JAN-2007' FROM DUAL:
- F. SELECT TO_DATE(SYSDAT
- G. *DD/MONTH/YYYY') - '01/JANUARY/2007' FROM DUAL:
Answer: BC
NEW QUESTION 6
The DBA issues this SQL command:
CREATE USER Scott
IDENTIFIED by tiger;
What privileges does the user Scott have at this point?
- A. No privilege
- B. Only the SELECT privileg
- C. Only the CONNECT privileg
- D. All the privileges of a default use
Answer: A
Explanation:
There are no privileges for the user Scott at this point. They are not added themselves to
the user immediately after creation. The DBA needs to grant all privileges explicitly.
Incorrect Answers
B:There are no privileges for the user Scott at this point. SELECT privilege needs to be
added to the user Scott.
C:There are no privileges for the user Scott at this point. CONNECT privilege needs to be
added to the user Scott.
D:There is no default user in Oracle.
OCP Introduction to Oracle 9i: SQL Exam Guide, Jason Couchman, p. 348-351
Chapter 8: User Access in Oracle
NEW QUESTION 7
Examine the structure of the EMPLOYEES table: 
Which INSERT statement is valid?
- A. INSERT INTO employees (employee_id, first_name, last_name, hire_date) VALUES ( 1000, ‘John’, ‘Smith’, ‘01/01/01’);
- B. INSERT INTO employees(employee_id, first_name, last_name, hire_date) VALUES ( 1000, ‘John’, ‘Smith’, ’01 January 01’);
- C. INSERT INTO employees(employee_id, first_name, last_name, Hire_date) VALUES ( 1000, ‘John’, ‘Smith’, To_date(‘01/01/01’));
- D. INSERT INTO employees(employee_id, first_name, last_name, hire_date) VALUES ( 1000, ‘John’, ‘Smith’, 01-Jan-01);
Answer: D
Explanation: It is the only statement that has a valid date; all other will result in an error. Answer A is incorrect, syntax error, invalid date format
NEW QUESTION 8
Which statement is true regarding transactions? (Choose all that apply.)
- A. A transaction can consist only of a set of DML and DDL statement
- B. A part or an entire transaction can be undone by using ROLLBACK comman
- C. A transaction consists of a set of DML or DCL statement
- D. A part or an entire transaction can be made permanent with a COMMI
- E. A transaction can consist of only a set of queries or DML or DDL statement
Answer: BC
NEW QUESTION 9
View the Exhibits and examine the structures of the COSTS and PROMOTIONS tables. 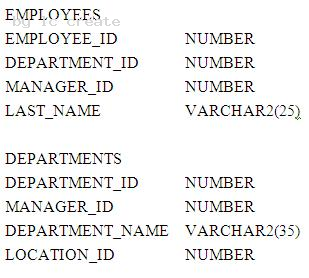
Evaluate the following SQL statement:
SQL> SELECT prod_id FROM costs WHERE promo_id IN (SELECT promo_id FROM promotions WHERE promo_cost < ALL (SELECT MAX(promo_cost) FROM promotions GROUP BY (promo_end_datepromo_ begin_date)));
What would be the outcome of the above SQL statement?
- A. It displays prod IDs in the promo with the lowest cos
- B. It displays prod IDs in the promos with the lowest cost in the same time interva
- C. It displays prod IDs in the promos with the highest cost in the same time interva
- D. It displays prod IDs in the promos with cost less than the highest cost in the same time interva
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 10
View the Exhibit and examine the structure of the PRODUCTS table. 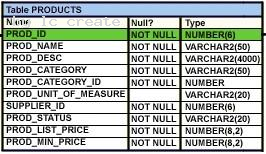
You want to display the category with the maximum number of items. You issue the following query:
SQL>SELECT COUNT(*),prod_category_id FROM products GROUP BY prod_category_id HAVING COUNT(*) = (SELECT MAX(COUNT(*)) FROM products);
What is the outcome?
- A. It executes successfully and gives the correct outpu
- B. It executes successfully but does not give the correct outpu
- C. It generates an error because the subquery does not have a GROUP BY claus
- D. It generates an error because = is not valid and should be replaced by the IN operato
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 11
Which view should a user query to display the columns associated with the constraints on a table owned by the user?
- A. USER_CONSTRAINTS
- B. USER_OBJECTS
- C. ALL_CONSTRAINTS
- D. USER_CONS_COLUMNS
- E. USER_COLUMNS
Answer: D
Explanation: view the columns associated with the constraint names in the USER_CONS_COLUMNS view. Incorrect Answer: Atable to view all constraints definition and names Bshow all object name belong to user Cdoes not display column associated Eno such view
Refer: Introduction to Oracle9i: SQL, Oracle University Study Guide, 10-25
NEW QUESTION 12
View the Exhibit and examine the structure of ORDERS and CUSTOMERS tables. 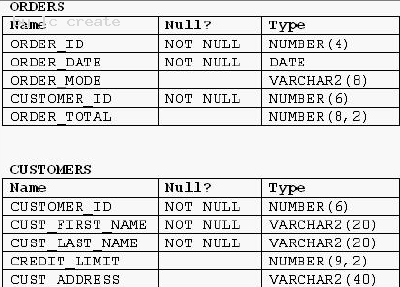
There is only one customer with the CUST_LAST_NAME column having value Roberts. Which INSERT statement should be used to add a row into the ORDERS table for the customer whose CUST_LAST_NAME is Roberts and CREDIT_LIMIT is 600?
- A. INSERT INTO orders VALUES (1,'10-mar-2007', 'direct', (SELECT customer_id FROM customers WHERE cust_last_name='Roberts' AND credit_limit=600), 1000);
- B. INSERT INTO orders (order_id,order_date,order_mode, (SELECT customer_id FROM customers WHERE cust_last_name='Roberts' AND credit_limit=600),order_total) VALUES(1,'10-mar-2007', 'direct', &&customer_id, 1000);
- C. INSERT INTO(SELECT o.order_id, o.order_date,o.order_mode,c.customer_id, o.order_total FROM orders o, customers c WHERE o.customer_id = c.customer_id AND c.cust_last_name='Roberts' ANDc.credit_limit=600 ) VALUES (1,'10-mar-2007', 'direct',(SELECT customer_id FROM customers WHERE cust_last_name='Roberts' AND credit_limit=600), 1000);
- D. INSERT INTO orders (order_id,order_date,order_mode, (SELECT customer_id FROM customers WHERE cust_last_name='Roberts' AND credit_limit=600),order_total) VALUES(1,'10-mar-2007', 'direct', &customer_id, 1000);
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 13
View the Exhibit to examine the description for the SALES table. Which views can have all DML operations performed on it? (Choose all that apply.) 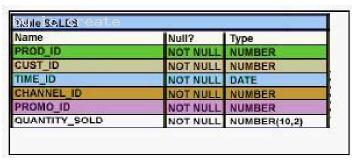
- A. CREATE VIEW v3 AS SELECT * FROM SALES WHERE cust_id = 2034 WITH CHECK OPTION;
- B. CREATE VIEW v1 AS SELECT * FROM SALES WHERE time_id <= SYSDATE - 2*365 WITH CHECK OPTION;
- C. CREATE VIEW v2 AS SELECT prod_id, cust_id, time_id FROM SALES WHERE time_id <= SYSDATE - 2*365 WITH CHECK OPTION;
- D. CREATE VIEW v4 AS SELECT prod_id, cust_id, SUM(quantity_sold) FROM SALES WHERE time_id <= SYSDATE - 2*365 GROUP BY prod_id, cust_id WITH CHECK OPTION;
Answer: AB
Explanation:
Creating a View You can create a view by embedding a subquery in the CREATE VIEW statement. In the syntax: CREATE [OR REPLACE] [FORCE|NOFORCE] VIEW view [(alias[, alias]...)] AS subquery [WITH CHECK OPTION [CONSTRAINT constraint]] [WITH READ ONLY [CONSTRAINT constraint]]; OR REPLACE Re-creates the view if it already exists FORCE Creates the view regardless of whether or not the base tables exist NOFORCE Creates the view only if the base tables exist (This is the default.) View Is the name of the view alias Specifies names for the expressions selected by the view’s query (The number of aliases must match the number of expressions selected by the view.) subquery Is a complete SELECT statement (You can use aliases for the columns in the SELECT list.) WITH CHECK OPTION Specifies that only those rows that are accessible to the view can be inserted or updated ANSWER D constraint Is the name assigned to the CHECK OPTION constraint WITH READ ONLY Ensures that no DML operations can be performed on this view Rules for Performing DML Operations on a View You cannot add data through a view if the view includes: Group functions A GROUP BY clause The DISTINCT keyword The pseudocolumn ROWNUM keyword Columns defined by expressions NOT NULL columns in the base tables that are not selected by the view – ANSWER C
NEW QUESTION 14
Which two statements are true regarding indexes? (Choose two.)
- A. They can be created on tables and cluster
- B. They can be created on tables and simple view
- C. You can create only one index by using the same column
- D. You can create more than one index by using the same columns if you specify distinctly different combinations of the column
Answer: AD
NEW QUESTION 15
Which three statements are true regarding sub queries? (Choose three.)
- A. Multiple columns or expressions can be compared between the main query and sub query
- B. Sub queries can contain GROUP BY and ORDER BY clauses
- C. Only one column or expression can be compared between the main query and subqeury
- D. Main query and sub query can get data from different tables
- E. Main query and sub query must get data from the same tables
- F. Sub queries can contain ORDER BY but not the GROUP BY clause
Answer: ABD
NEW QUESTION 16
View the Exhibit and examine the structure of the SALES table.
The following query is written to retrieve all those product IDs from the SALES table that have more than 55000 sold and have been ordered more than 10 times. 
Which statement is true regarding this SQL statement? 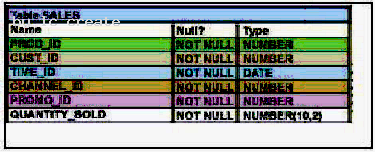
- A. It executes successfully and generates the required resul
- B. It produces an error because COUNT(*) should be specified in the SELECT clause als
- C. It produces an error because COUNT(*) should be only in the HAVING clause and not in the WHERE claus
- D. It executes successfully but produces no result because COUNT(prod_id) should be used instead of COUNT(*).
Answer: C
Explanation:
Restricting Group Results with the HAVING Clause
You use the HAVING clause to specify the groups that are to be displayed, thus further
restricting the groups on the basis of aggregate information.
In the syntax, group_condition restricts the groups of rows returned to those groups for
which the specified condition is true.
The Oracle server performs the following steps when you use the HAVING clause:
1.
Rows are grouped.
2.
The group function is applied to the group.
3.
The groups that match the criteria in the HAVING clause are displayed.
The HAVING clause can precede the GROUP BY clause, but it is recommended that you
place the GROUP BY clause first because it is more logical. Groups are formed and group
functions are calculated before the HAVING clause is applied to the groups in the SELECT
list.
Note: The WHERE clause restricts rows, whereas the HAVING clause restricts groups.
NEW QUESTION 17
Examine the structure of the PRODUCTS table: 
You want to display the names of the products that have the highest total value for UNIT_PRICE *QTY_IN_HAND.
Which SQL statement gives the required output?
- A. SELECT prod_name FROM products WHERE (unit_price * qty_in_hand) = (SELECT MAX(unit_price * qty_in_hand) FROM products);
- B. SELECT prod_name FROM products WHERE (unit_price * qty_in_hand) = (SELECT MAX(unit_price * qty_in_hand) FROM products GROUP BY prod_name);
- C. SELECT prod_name FROM products GROUP BY prod_name HAVING MAX(unit_price * qty_in_hand) = (SELECT MAX(unit_price * qty_in_hand) FROM products GROUP BY prod_name);
- D. SELECT prod_name FROM products WHERE (unit_price * qty_in_hand) = (SELECT MAX(SUM(unit_price * qty_in_hand)) FROM products) GROUP BY prod_name;
Answer: A
100% Valid and Newest Version 1Z0-051 Questions & Answers shared by Surepassexam, Get Full Dumps HERE: https://www.surepassexam.com/1Z0-051-exam-dumps.html (New 292 Q&As)
