2V0-41.23 Exam
How Many Questions Of 2V0-41.23 Answers

Downloadable of 2V0-41.23 free question materials and practice for VMware certification for IT specialist, Real Success Guaranteed with Updated 2V0-41.23 pdf dumps vce Materials. 100% PASS VMware NSX 4.x Professional exam Today!
Free demo questions for VMware 2V0-41.23 Exam Dumps Below:
NEW QUESTION 1
When collecting support bundles through NSX Manager, which files should be excluded for potentially containing sensitive information?
- A. Controller Files
- B. Management Files
- C. Core Files
- D. Audit Files
Answer: C
Explanation:
According to the VMware NSX Documentation1, core files and audit logs can contain sensitive information and should be excluded from the support bundle unless requested by VMware technical support. Controller files and management files are not mentioned as containing sensitive information.
NEW QUESTION 2
An NSX administrator would like to export syslog events that capture messages related to NSX host preparation events. Which message ID (msgld) should be used in the syslog export configuration command as a filler?
- A. MONISTORING
- B. SYSTEM
- C. GROUPING
- D. FABRIC
Answer: D
Explanation:
According to the VMware NSX Documentation2, the FABRIC message ID (msgld) captures messages related to NSX host preparation events, such as installation, upgrade, or uninstallation of NSX components on ESXi hosts. The syslog export configuration command for NSX host preparation events would look something like this:
set service syslog export FABRIC
The other options are either incorrect or not relevant for NSX host preparation events. MONITORING captures messages related to NSX monitoring features, such as alarms and system events2. SYSTEM captures messages related to NSX system events, such as login, logout, or configuration changes2. GROUPING captures messages related to NSX grouping objects, such as security groups, security tags, or IP sets2.
https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX/4.1/administration/GUID-CC18C0E3-D076-41AA-8B8C-133650FD
NEW QUESTION 3
Which CLI command on NSX Manager and NSX Edge is used to change NTP settings?
- A. get timezone
- B. get time-server
- C. set timezone
- D. set ntp-server
Answer: D
Explanation:
The CLI command on NSX Manager and NSX Edge that is used to change NTP settings is set ntp-server. Th command allows the user to configure one or more NTP servers for time synchronization12. The other options are incorrect because they are not valid CLI commands for changing NTP settings. The get timezone and timezone commands are used to display and configure the timezone of the system1. The get
time-server command is used to display the current time server configuration1. There are no CLI commands for using RADIUS or BootP for NTP settings. References: NSX-T Command-Line Interface
Reference, vSphere ESXi 7.0 U3 and later versions NTP configuration steps
NEW QUESTION 4
Which two choices are use cases for Distributed Intrusion Detection? (Choose two.)
- A. Use agentless antivirus with Guest Introspection.
- B. Quarantine workloads based on vulnerabilities.
- C. Identify risk and reputation of accessed websites.
- D. Gain Insight about micro-segmentation traffic flows.
- E. Identify security vulnerabilities in the workloads.
Answer: BE
Explanation:
According to the VMware NSX Documentation, these are two of the use cases for Distributed Intrusion Detection, which is a feature of NSX Network Detection and Response: Quarantine workloads based on vulnerabilities: You can use Distributed Intrusion Detection to detect vulnerabilities in your workloads and apply quarantine actions to isolate them from the network until they are remediated.
Quarantine workloads based on vulnerabilities: You can use Distributed Intrusion Detection to detect vulnerabilities in your workloads and apply quarantine actions to isolate them from the network until they are remediated. Identify security vulnerabilities in the workloads: You can use Distributed Intrusion Detection to scan your workloads for known vulnerabilities and generate reports that show the severity, impact, and remediation steps for each vulnerability.
Identify security vulnerabilities in the workloads: You can use Distributed Intrusion Detection to scan your workloads for known vulnerabilities and generate reports that show the severity, impact, and remediation steps for each vulnerability.
NEW QUESTION 5
Which field in a Tier-1 Gateway Firewall would be used to allow access for a collection of trustworthy web sites?
- A. Source
- B. Profiles -> Context Profiles
- C. Destination
- D. Profiles -> L7 Access Profile
Answer: D
Explanation:
The field in a Tier-1 Gateway Firewall that would be used to allow access for a collection of trustworthy web sites is Profiles -> L7 Access Profile. This field allows the user to create a Layer 7 access profile that defines list of allowed or blocked URLs based on categories, reputation, or custom entries1. The user can then apply the L7 access profile to a firewall rule to control the traffic based on the URL filtering criteria1. The other options are incorrect because they are not related to URL filtering. The Source field specifies the source IP address or group of the firewall rule1. The Destination field specifies the destination IP address or group of the firewall rule1. The Profiles -> Context Profiles field allows the user to create a context profile that defines a list of application signatures or attributes that can be used to identify and classify network
traffic1. References: Gateway Firewall
NEW QUESTION 6
Refer to the exhibit.
An administrator configured NSX Advanced Load Balancer to redistribute the traffic between the web servers. However, requests are sent to only one server
Which of the following pool configuration settings needs to be adjusted to resolve the problem? Mark the correct answer by clicking on the image.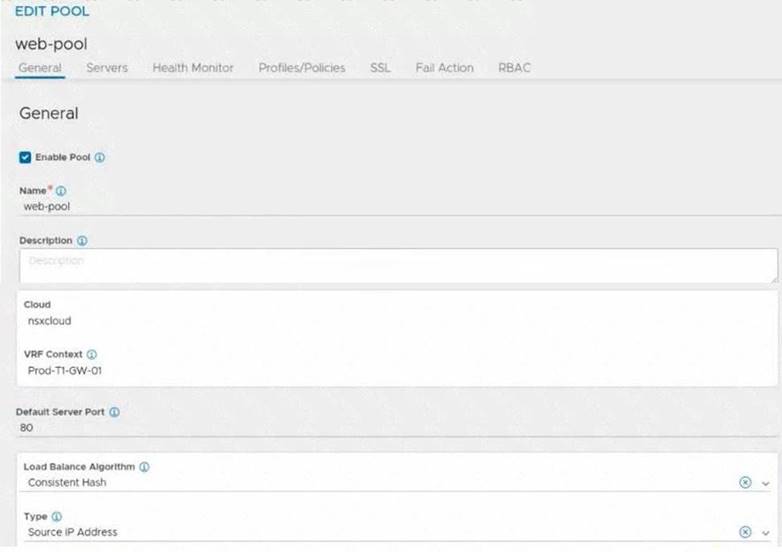
Solution:
Load Balancing Algorithm
Does this meet the goal?
- A. Yes
- B. Not Mastered
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 7
What are two supported host switch modes? (Choose two.)
- A. DPDK Datapath
- B. Enhanced Datapath
- C. Overlay Datapath
- D. Secure Datapath
- E. Standard Datapath
Answer: BE
Explanation:
The host switch modes determine how the NSX network and security stack is allocated on the underlying host CPU or DPU. There are two supported host switch modes: Enhanced Datapath and Standard
Datapath1. Enhanced Datapath mode leverages the DPU to offload the NSX datapath processing from the host CPU, while Standard Datapath mode uses the host CPU for the NSX datapath processing1. DPDK Datapath, Overlay Datapath, and Secure Datapath are not valid host switch modes for NSX 4.x. References: NSX Features
NEW QUESTION 8
Which command is used to set the NSX Manager's logging-level to debug mode for troubleshooting?
- A. Set service manager log-level debug
- B. Set service manager logging-level debug
- C. Set service nsx-manager log-level debug
- D. Set service nsx-manager logging-level debug
Answer: B
Explanation:
According to the VMware Knowledge Base article 1, the CLI command to set the log level of the NSX Manager to debug mode is set service manager logging-level debug. This command can be used when the NSX UI is inaccessible or when troubleshooting issues with the NSX Manager1. The other commands are incorrect because they either use a wrong syntax or a wrong service name. The NSX Manager service name is manager, not nsx-manager2. The log level parameter is logging-level, not log-level3.
https://kb.vmware.com/s/article/55868
NEW QUESTION 9
An administrator wants to validate the BGP connection status between the Tier-O Gateway and the upstream physical router.
What sequence of commands could be used to check this status on NSX Edge node?
- A. set vrf <ID>show logical-routers show <LR-D> bgp
- B. show logical-routers get vrfshow ip route bgp
- C. get gateways vrf <number>get bgp neighbor
- D. enable <LR-D> get vrf <ID>show bgp neighbor
Answer: C
Explanation:
The sequence of commands that could be used to check the BGP connection status between the Tier-O Gateway and the upstream physical router on NSX Edge node is get gateways, vrf <number>, get bgp neighbor. These commands can be executed on the NSX Edge node CLI after logging in as admin6. The firs command, get gateways, displays the list of logical routers (gateways) configured on the Edge node, along with their IDs and VRF numbers7. The second command, vrf <number>, switches to the VRF context of the desired Tier-O Gateway, where <number> is the VRF number obtained from the previous command7. The third command, get bgp neighbor, displays the BGP neighbor summary for the selected VRF, including the neighbor IP address, AS number, state, uptime, and prefixes received8. The other options are incorrect because they either use invalid or incomplete commands or do not switch to the correct VRF
context. References: NSX-T Command-Line Interface Reference, NSX Edge Node CLI Commands, Troubleshooting BGP on NSX-T Edge Nodes
NEW QUESTION 10
Which three DHCP Services are supported by NSX? (Choose three.)
- A. Gateway DHCP
- B. Port DHCP per VNF
- C. Segment DHCP
- D. VRF DHCP Server
- E. DHCP Relay
Answer: ACE
Explanation:
According to the VMware NSX Documentation1, NSX-T Data Center supports the following types of DHCP configuration on a segment: Local DHCP server: This option creates a local DHCP server that has an IP address on the segment and provides dynamic IP assignment service only to the VMs that are attached to the segment.
Local DHCP server: This option creates a local DHCP server that has an IP address on the segment and provides dynamic IP assignment service only to the VMs that are attached to the segment. Gateway DHCP server: This option is attached to a tier-0 or tier-1 gateway and provides DHCP service to the networks (overlay segments) that are directly connected to the gateway and configured to use a gateway DHCP server.
Gateway DHCP server: This option is attached to a tier-0 or tier-1 gateway and provides DHCP service to the networks (overlay segments) that are directly connected to the gateway and configured to use a gateway DHCP server. DHCP Relay: This option relays the DHCP client requests to the external DHCP servers that can be in any subnet, outside the SDDC, or in the physical network.
DHCP Relay: This option relays the DHCP client requests to the external DHCP servers that can be in any subnet, outside the SDDC, or in the physical network.
NEW QUESTION 11
As part of an organization's IT security compliance requirement, NSX Manager must be configured for 2FA (two-factor authentication).
What should an NSX administrator have ready before the integration can be configured? O
- A. Active Directory LDAP integration with OAuth Client added
- B. VMware Identity Manager with an OAuth Client added
- C. Active Directory LDAP integration with ADFS
- D. VMware Identity Manager with NSX added as a Web Application
Answer: B
Explanation:
To configure NSX Manager for two-factor authentication (2FA), an NSX administrator must have VMware
Identity Manager (vIDM) with an OAuth Client added. vIDM provides identity management services and supports various 2FA methods, such as VMware Verify, RSA SecurID, and RADIUS. An OAuth Client is a configuration entity in vIDM that represents an application that can use vIDM for authentication and authorization. NSX Manager must be registered as an OAuth Client in vIDM before it can use
2FA. References: : VMware NSX-T Data Center Installation Guide, page 19. : VMware NSX-T Data Center Administration Guide, page 102. : VMware Blogs: Two-Factor Authentication with VMware NSX-T
NEW QUESTION 12
A security administrator needs to configure a firewall rule based on the domain name of a specific application. Which field in a distributed firewall rule does the administrator configure?
- A. Profile
- B. Service
- C. Policy
- D. Source
Answer: A
Explanation:
To configure a firewall rule based on the domain name of a specific application, the administrator needs to use the Profile field in a distributed firewall rule. The Profile field allows the administrator to select a context profile that contains one or more attributes for filtering traffic. One of the attributes that can be used is Domain (FQDN) Name, which specifies the fully qualified domain name of the application. For example, if the administrator wants to filter traffic to *.office365.com, they can create a context profile with the Domain (FQDN) Name attribute set to *.office365.com and use it in the Profile field of the firewall rule.
References: Filtering Specific Domains (FQDN/URLs)
Filtering Specific Domains (FQDN/URLs)  FQDN Filtering
FQDN Filtering
NEW QUESTION 13
An NSX administrator is reviewing syslog and notices that Distributed Firewall Rules hit counts are not being logged.
What could cause this issue?
- A. Syslog is not configured on the ESXi transport node.
- B. Zero Trust Security is not enabled.
- C. Syslog is not configured on the NSX Manager.
- D. Distributed Firewall Rule logging is not enabled.
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 14
An NSX administrator Is treating a NAT rule on a Tler-0 Gateway configured In active-standby high availability mode. Which two NAT rule types are supported for this configuration? (Choose two.)
- A. Reflexive NAT
- B. Destination NAT
- C. 1:1 NAT
- D. Port NAT
- E. Source NAT
Answer: BE
Explanation:
According to the VMware NSX Documentation, these are two NAT rule types that are supported for a tier-0 gateway configured in active-standby high availability mode. NAT stands for Network Address Translation and is a feature that allows you to modify the source or destination IP address of a packet as it passes through a gateway. Destination NAT: This rule type allows you to change the destination IP address of a packet from an external IP address to an internal IP address. You can use this rule type to provide access to your internal servers from external networks using public IP addresses.
Destination NAT: This rule type allows you to change the destination IP address of a packet from an external IP address to an internal IP address. You can use this rule type to provide access to your internal servers from external networks using public IP addresses. Source NAT: This rule type allows you to change the source IP address of a packet from an internal IP address to an external IP address. You can use this rule type to provide access to external networks from your internal servers using public IP addresses.
Source NAT: This rule type allows you to change the source IP address of a packet from an internal IP address to an external IP address. You can use this rule type to provide access to external networks from your internal servers using public IP addresses.
NEW QUESTION 15
Which command Is used to test management connectivity from a transport node to NSX Manager?
- A. esxcli network ip connection list | grep 1234

- B. esxcli network connection list | grep 1235

- C. esxcli network ip connection list | grep 1235
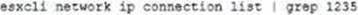
- D. esxcli network connection list | grep 1234

Answer: A
Explanation:
The NSX Manager management plane communicates with the transport nodes by using APH Server over NSX-RPC/TCP through port 1234. CCP communicates with the transport nodes by using APH Server over NSX-RPC/TCP through port 1235.
NEW QUESTION 16
An architect receives a request to apply distributed firewall in a customer environment without making changes to the network and vSphere environment. The architect decides to use Distributed Firewall on VDS.
Which two of the following requirements must be met in the environment? (Choose two.)
- A. vCenter 8.0 and later
- B. NSX version must be 3.2 and later
- C. NSX version must be 3.0 and later
- D. VDS version 6.6.0 and later
Answer: BD
Explanation:
Distributed Firewall on VDS is a feature of NSX-T Data Center that allows users to install Distributed Security for vSphere Distributed Switch (VDS) without the need to deploy an NSX Virtual Distributed Switch (N-VDS). This feature provides NSX security capabilities such as Distributed Firewall (DFW), Distributed IDS/IPS, Identity Firewall, L7 App ID, FQDN Filtering, NSX Intelligence, and NSX Malware Prevention. To enable this feature, the following requirements must be met in the environment: The NSX version must be 3.2 and later1. This is the minimum version that supports Distributed Security for VDS.
The NSX version must be 3.2 and later1. This is the minimum version that supports Distributed Security for VDS. The VDS version must be 6.6.0 and later1. This is the minimum version that supports the NSX host preparation operation that activates the DFW with the default rule set to allow.
The VDS version must be 6.6.0 and later1. This is the minimum version that supports the NSX host preparation operation that activates the DFW with the default rule set to allow.
References: Overview of NSX IDS/IPS and NSX Malware Prevention
Overview of NSX IDS/IPS and NSX Malware Prevention
NEW QUESTION 17
What are tour NSX built-in rote-based access control (RBAC) roles? (Choose four.)
- A. Network Admin
- B. Enterprise Admin
- C. Full Access
- D. Read
- E. LB Operator
- F. None
- G. Auditor
Answer: ABEG
Explanation:
https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX/4.1/administration/GUID-26C44DE8-1854-4B06-B6DA-A2FD426
NEW QUESTION 18
......
P.S. Easily pass 2V0-41.23 Exam with 106 Q&As DumpSolutions.com Dumps & pdf Version, Welcome to Download the Newest DumpSolutions.com 2V0-41.23 Dumps: https://www.dumpsolutions.com/2V0-41.23-dumps/ (106 New Questions)
