642-889 Exam
Improve 642-889 Training Materials 2021

Act now and download your Cisco 642-889 test today! Do not waste time for the worthless Cisco 642-889 tutorials. Download Up to date Cisco Implementing Cisco Service Provider Next-Generation Edge Network Services (SPEDGE) exam with real questions and answers and begin to learn Cisco 642-889 with a classic professional.
Free 642-889 Demo Online For Cisco Certifitcation:
NEW QUESTION 1
When implementing EoMPLS on Cisco IOS XR routers, which command under the l2vpn configuration mode is used to define the pseudowire?
- A. pbb
- B. xconnect
- C. connect
- D. bridge
- E. bridge-domain
Answer: B
Explanation:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/wireless/asr_901/Configuration/Guide/eompls.html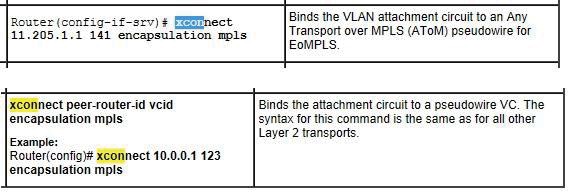
NEW QUESTION 2
A network engineer working for a very large financial institution must migrate the legacy Frame Relay and ATM virtual circuits over a MPLS VPN solution. Which option is a benefit in choosing a MPLS Layer 3 VPN versus any other Layer 2 VPN design?
- A. An MPLS Layer 3 VPN design offers better scalability for large organizations.
- B. An MPLS Layer 3 VPN design requires less customer edge router configuration than any other Layer 2 VPN implementation.
- C. An MPLS Layer 3 VPN solution provides the possibility to implement overlapping IP addressing.
- D. An MPLS Layer 3 VPN design requires less provider edge router configuration than any other Layer 2 VPN implementation.
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 3
What is the primary difference between 6PE and 6VPE?
- A. 6VPE does not require an MPLS core.
- B. 6VPE requires an IPv6-aware core.
- C. 6VPE provides IPv6 VPN services.
- D. 6VPE tunnels IPv6 packets inside IPv4 packets.
Answer: C
Explanation:
6PE is for transporting ipv6 natively and 6VPE is for ipv6 mpls vpns
NEW QUESTION 4
Which two Layer 2 VPN methods support interworking between customer sites with different Layer 2 encapsulation at each end {for example, Frame Relay to Ethernet interworking}? {Choose two.}
- A. AToM
- B. VPLS
- C. GET VPN
- D. L2TPv3
Answer: AD
Explanation:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_3t/12_3t2/feature/guide/gtl2tpv3.html#wp1040784
The Layer 2 Tunnel Protocol Version 3 feature expands on Cisco support of the Layer 2 Tunnel Protocol Version 3 {L2TPv3}. L2TPv3 is an Internet Engineering Task Force {IETF} l2tpext working group draft that provides several enhancements to L2TP for the capability to tunnel any Layer 2 payload over L2TP.
Specifically, L2TPv3 defines the L2TP protocol for tunneling Layer 2 payloads over an IP core network using Layer 2 virtual private networks {VPNs}. Benefits of this feature include the following:
•L2TPv3 simplifies deployment of VPNs
•L2TPv3 does not require Multiprotocol Label Switching
•L2TPv3 supports Layer 2 tunneling over IP for any payload http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6646/products_ios_protocol_option_home.html
Cisco Any Transport over MPLS {AToM} is a solution for transporting Layer 2 packets over an MPLS backbone. It enables Service Providers to supply connectivity between customer sites with existing data link layer {Layer 2} networks via a single, integrated, packet-based network infrastructure: a Cisco MPLS network. Without separate networks that each have network management environments, Service Providers can deliver Layer 2 connections over an MPLS backbone.
Cisco AToM provides a common framework to encapsulate and transport supported Layer 2 traffic types over an MPLS network core. Service Providers can use a single MPLS network infrastructure to offer connectivity for supported Layer 2 traffic and for IP traffic in Layer 3 VPNs.
NEW QUESTION 5
When implementing MPLS Layer 3 VPNs with customers running OSPF as the CE-PE routing protocol, which situation will require a sham link to be implemented in the MPLS backbone?
- A. to connect customer sites in different OSPF areas
- B. to connect customer sites in the same OSPF area
- C. to prevent OSPF routing loops when a customer site has redundant CE-PE connections
- D. if there is a backdoor link between the CE routers, to ensure that the backdoor link is used only to back up the primary connection through the MPLS VPN
Answer: D
Explanation:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_2t/12_2t8/feature/guide/ospfshmk.html
NEW QUESTION 6
Which method can be used to discover targeted LDP neighbors dynamically when configuring VPLS between PE routers?
- A. BGP autodiscovery
- B. VPLS peers under the VFI
- C. VPWS
- D. BGP
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 7
In Layer 3 MPLS VPN implementations, which protocol is used to carry the VPNv4 routes from PE to PE?
- A. RSVP
- B. IGP
- C. MP-BGP
- D. LDP
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 8
Which protocol is used to hide customer VLANs inside the provider backbone network?
- A. 802.1ap
- B. 802.1x
- C. 802.1ad
- D. 802.1q
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 9
In MPLS Layer 3 VPN implementations, which mechanism is used to control which routes are imported to a VRF?
- A. RT
- B. RD
- C. VC ID
- D. PW ID
- E. VRF ID
Answer: A
Explanation:
http://blog.initialdraft.com/archives/1537/
NEW QUESTION 10
Refer the exhibit.
On PE7, which three statements are correct regarding the MPLS VPN configurations used to support the connectivity between the CE7 and CE8 sites? {Choose three.}
- A. The RD is 1:1
- B. The import and export RTs are 1:1
- C. Interface GiO/0/0/0 is associated to the "default" VRF
- D. The network that connects PE7to CE7 is redistributed into multiprotocol IBGP
- E. The multiprotocol IBGP routes learned have a BGP origin code of "i"
Answer: BCE
Explanation:
# show ip route show ip vrf
show ip vrf detail
NEW QUESTION 11
Refer the exhibit.
On PE7, which interface connects to the CE7 and what is the name of the VRF that interface is associated to? {Choose two.}
- A. Gi0/0/0/0
- B. Gi0/0/0/1
- C. Gi0/0/0/2
- D. Customer_1
- E. Customer_A
- F. Customer_CE7
Answer: BC
Explanation:
# show ip vrf interfaces
NEW QUESTION 12
Which option is a valid Cisco IOS XR BGP Layer 3 IPv4 MPLS VPN configuration?
- A. router bgp 65001no bgp default ipv4-unicast bgp log-neighbor-changesneighbor 1.2.3.4 remote-as 65001 neighbor 1.2.3.4 update-source Loopback0 address-family vpnv4neighbor 1.2.3.4 activateneighbor 1.2.3.4 send-community extended exit-address-familyaddress-family ipv4 vrf VPN redistribute ospf 100
- B. router bgp 65001no bgp default ipv4-unicast bgp log-neighbor-changesneighbor 1.2.3.4 remote-as 65001 neighbor 1.2.3.4 update-source Loopback0 address-family vpnv4neighbor 1.2.3.4 activate exit-address-familyaddress-family ipv4 vrf VPN redistribute ospf 100
- C. router bgp 100address-family vpnv4 unicast neighbor 2.2.2.2remote-as 100update-source Loopback0 address-family vpnv4 unicast!vrf VPN_A rd 100:1address-family ipv4 unicast redistribute ospf 100
- D. router bgp 100address-family vpnv4 unicast neighbor 2.2.2.2remote-as 100update-source Loopback0 address-family ipv4 unicast!vrf VPN_A rd 100:1address-family ipv4 unicast redistribute ospf 100
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 13
Which two MPLS QoS models described by RFC3270 are used for CE-PE QoS implementation? {Choose two.}
- A. best effort
- B. pipe
- C. uniform
- D. integrated services
- E. differentiated services
Answer: BC
NEW QUESTION 14
Refer to the exhibit.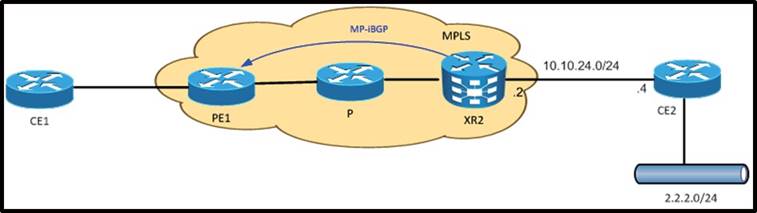
XR2 must be configured with a static route for 2.2.2.0/24 subnet toward CE2 into the VRF ABC table. Which configuration achieves this goal?
- A. router static vrf ABC2.2.2.0/24 10.10.24.2
- B. router static vrf ABC2.2.2.0/24 10.10.24.2address-family ipv4 unicast
- C. router static vrf ABCaddress-family ipv4 unicast 2.2.2.0/24 10.10.24.2
- D. router staticaddress-family ipv4 unicast vrf ABC2.2.2.0/24 10.10.24.2
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 15
In which Cisco IOS XR configuration mode is the redistribute static command applied to enable the redistribution of static VRF routes between the PE routers?
- A. RP/0/RP0/CPU0:PE{config-router}#
- B. RP/0/RP0/CPU0:PE{config-bgp}#
- C. RP/0/RP0/CPU0:PE{config-bgp-vrf}#
- D. RP/0/RP0/CPU0:PE{config-bgp-vrf-af}#
Answer: D
Explanation:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/routers/asr9000/software/routing/configuration/guide/rcasr9kstat.html#wp1041 359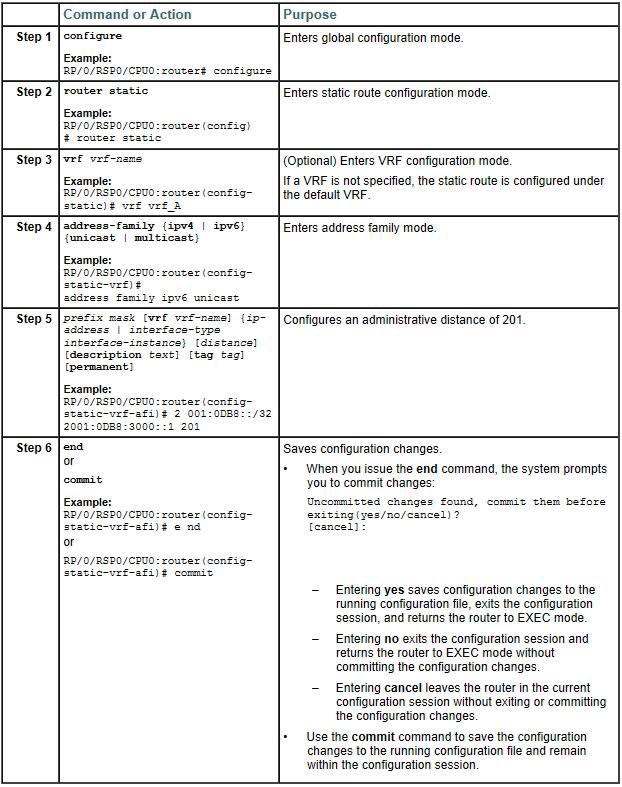
NEW QUESTION 16
Refer to the partial Cisco IOS XR PE router configuration exhibit for supporting a Layer 3 MPLS VPN customer using BGP as the CE-to-PE routing protocol.
The service provider AS number is 64500, the customer AS number is 64501, and the customer CE router is 10.1.1.1. What is missing in the configuration?
- A. The route distinguisher has not been configured under router bgp 64500 vrf Customer_A.
- B. The import and export route targets have not been configured under router bgp 64500 vrf Customer_A.
- C. The 10.1.1.1 BGP neighbor has not been activated for IPv4 unicast routing.
- D. The 10.1.1.1 BGP neighbor has not been activated for the VPNv4 address family.
Answer: A
Explanation:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_2sr/12_2sra/feature/guide/srbgprid.html Route Distinguisher
A router distinguisher {RD} creates routing and forwarding tables and specifies the default route distinguisher for a VPN. The RD is added to the beginning of an IPv4 prefix to change it into a globally unique VPN-IPv4 prefix. An RD can be composed in one of two ways: with an autonomous system number and an arbitrary number or with an IP address and an arbitrary number. You can enter an RD in either of these formats:
•Enter a 16-bit autonomous system number, a colon, and a 32-bit number. For example: 45000:3
•Enter a 32-bit IP address, a colon, and a 16-bit number. For example: 192.168.10.15:1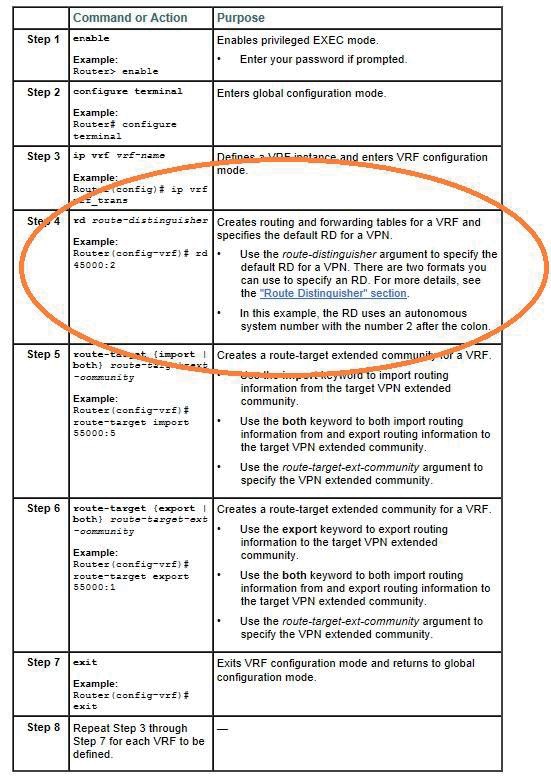
NEW QUESTION 17
A customer wants two separated sites to be connected via a pseudo-wire. Which solution provides the simplest implementation?
- A. AToM
- B. Layer 3 VPN
- C. VPLS
- D. GETVPN
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 18
VPWS/EoMPLS offers which type of Ethernet services as defined by the MEF?
- A. E-Tree
- B. E-LAN
- C. E-Line
- D. E-Interworking
Answer: C
Explanation:
• E-Line is based on a point-to-point Ethernet Virtual Connection. Two E-Line services are defined:
- Ethernet Private Line {EPL}: A very simple and basic point-to-point service characterized by low frame delay, frame delay variation, and frame loss ratio. No service multiplexing is allowed, and other than a committed information rate {CIR} no class of service {CoS} {Bandwidth Profiling} is allowed.
- Ethernet Virtual Private Line {EVPL}: A point-to-point service wherein service multiplexing {more than one Ethernet Virtual Connection} is allowed. The individual Ethernet Virtual Circuits can be defined with a rich set of Bandwidth Profiles and Layer 2 Control Protocol Processing methods as defined by the Metro Ethernet Forum.
NEW QUESTION 19
Which two methods can be used for VPLS PW signaling? {Choose two.}
- A. static
- B. BGP
- C. IGP
- D. LDP
- E. RSVP
Answer: BD
Explanation: 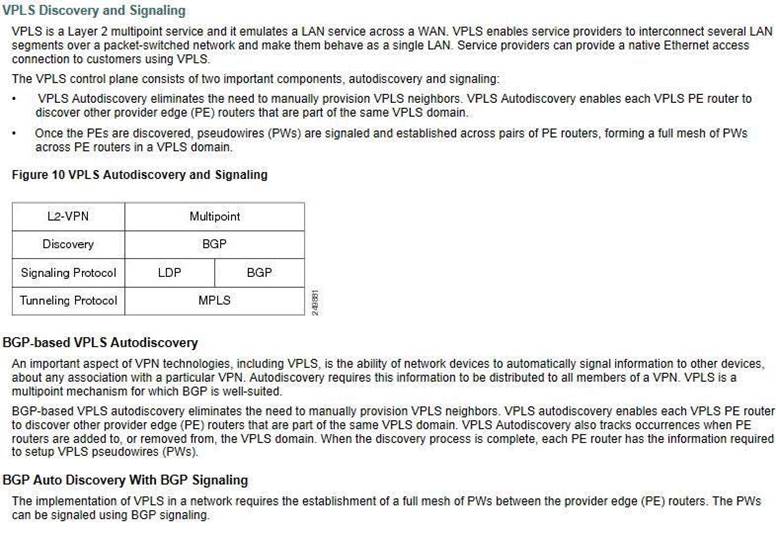
NEW QUESTION 20
A customer requests Internet through its MPLS provider. Which Internet design model guarantees maximum security and easier provisioning?
- A. Internet access through global routing
- B. Internet access through route leaking
- C. Internet access through a separate VPN service
- D. Internet access through multisite
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 21
......
P.S. Easily pass 642-889 Exam with 126 Q&As Certifytools Dumps & pdf Version, Welcome to Download the Newest Certifytools 642-889 Dumps: https://www.certifytools.com/642-889-exam.html (126 New Questions)
