DOP-C01 Exam
Top Tips Of Updated DOP-C01 Practice

Your success in Amazon-Web-Services DOP-C01 is our sole target and we develop all our DOP-C01 braindumps in a way that facilitates the attainment of this target. Not only is our DOP-C01 study material the best you can find, it is also the most detailed and the most updated. DOP-C01 Practice Exams for Amazon-Web-Services DOP-C01 are written to the highest standards of technical accuracy.
Also have DOP-C01 free dumps questions for you:
NEW QUESTION 1
Which of the following are Lifecycle events available in Opswork? Choose 3 answers from the options below
- A. Setup
- B. Decommision
- C. Deploy
- D. Shutdown
Answer: ACD
Explanation:
Below is a snapshot of the Lifecycle events in Opswork.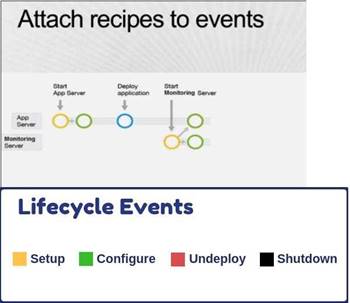
For more information on Lifecycle events, please refer to the below URL:
• http://docs.aws.amazon.com/opsworks/latest/userguide/workingcookbook-events.html
NEW QUESTION 2
You have a code repository that uses Amazon S3 as a data store. During a recent audit of your security controls, some concerns were raised about maintaining the integrity of the data in the Amazon S3 bucket. Another concern was raised around securely deploying code from Amazon S3 to applications running on Amazon EC2 in a virtual private cloud. What are some measures that you can implement to mitigate these concerns? Choose two answers from the options given below.
- A. Add an Amazon S3 bucket policy with a condition statement to allow access only from Amazon EC2 instances with RFC 1918 IP addresses and enable bucket versioning.
- B. Add an Amazon S3 bucket policy with a condition statement that requires multi-factor authentication in order to delete objects and enable bucket versioning.
- C. Use a configuration management service to deploy AWS Identity and Access Management user credentials to the Amazon EC2 instance
- D. Use these credentials to securely access the Amazon S3 bucket when deploying code.
- E. Create an Amazon Identity and Access Management role with authorization to access the Amazon S3 bucket, and launch all of your application's Amazon EC2 instances with this role.
- F. Use AWS Data Pipeline to lifecycle the data in your Amazon S3 bucket to Amazon Glacier on a weekly basis.
- G. Use AWS Data Pipeline with multi-factor authentication to securely deploy code from the Amazon S3 bucket to your Amazon EC2 instances.
Answer: BD
Explanation:
You can add another layer of protection by enabling MFA Delete on a versioned bucket. Once you do
so, you must provide your AWS account's access keys and a
valid code from the account's MFA device in order to permanently delete an object version or suspend or reactivate versioning on the bucket.
For more information on MFA please refer to the below link: https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/security/securing-access-to-aws-using-mfa-part-3/
IAM roles are designed so that your applications can securely make API requests from your instances, without requiring you to manage the security credentials that the applications use. Instead of creating and distributing your AWS credentials, you can delegate permission to make API requests using 1AM roles For more information on Roles for CC2 please refer to the below link: http://docs.aws.a mazon.com/AWSCC2/latest/UserGuide/iam-roles-for-amazon-ec2. htmI
Option A is invalid because this will not address either the integrity or security concern completely. Option C is invalid because user credentials should never be used in CC2 instances to access AWS resources.
Option C and F are invalid because AWS Pipeline is an unnecessary overhead when you already have inbuilt controls to manager security for S3.
NEW QUESTION 3
You are Devops Engineer for a large organization. The company wants to start using Cloudformation templates to start building their resources in AWS. You are getting requirements for the templates from various departments, such as the networking, security, application etc. What is the best way to architect these Cloudformation templates.
- A. Usea single Cloudformation template, since this would reduce the maintenanceoverhead on the templates itself.
- B. Createseparate logical templates, for example, a separate template for networking,security, application et
- C. Then nest the relevant templates.
- D. Considerusing Elastic beanstalk to create your environments since Cloudformation is notbuilt for such customization.
- E. Considerusing Opsworks to create your environments since Cloudformation is not builtfor such customization.
Answer: B
Explanation:
The AWS documentation mentions the following
As your infrastructure grows, common patterns can emerge in which you declare the same components in each of your templates. You can separate out these
common components and create dedicated templates for them. That way, you can mix and match different templates but use nested stacks to create a single, unified stack. Nested stacks are stacks that create other stacks. To create nested stacks, use the AWS::
Cloud Form ation::Stackresource in your template to reference other templates.
For more information on Cloudformation best practises, please visit the below url http://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCIoudFormation/latest/UserGuide/best-practices.html
NEW QUESTION 4
You have decided that you need to change the instance type of your production instances which are running as part of an AutoScaling group. The entire architecture is deployed using CloudFormation Template. You currently have 4 instances in Production. You cannot have any interruption in service and need to ensure 2 instances are always runningduring the update? Which of the options below listed can be used for this?
- A. AutoScalingRollingUpdate
- B. AutoScalingScheduledAction
- C. AutoScalingReplacingUpdate
- D. AutoScalinglntegrationUpdate
Answer: A
Explanation:
The AWS::AutoScaling::AutoScalingGroup resource supports an UpdatePoIicy attribute. This is used to define how an Auto Scalinggroup resource is updated when an update to the Cloud Formation stack occurs. A common approach to updating an Auto Scaling group is to perform a rolling update, which is done by specifying the AutoScalingRollingUpdate policy. This retains the same Auto Scaling group and replaces old instances with new ones, according to the parameters specified. For more information on Autoscaling updates, please refer to the below link: https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/knowledge-center/auto-scaling-group-rolling-updates/
NEW QUESTION 5
Which of the following are true with regard to Opsworks stack Instances? Choose 3 answers from the options given below.
- A. Astacks instances can be a combination of both Linux and Windows based operatingsystems.
- B. You can use EC2 Instances that were createdoutisde the boundary of Opswork.
- C. Youcanuseinstancesrunningonyourownhardware.
- D. Youcan start and stop instances manually.
Answer: BCD
Explanation:
The AWS Documentation mentions the following
1) You can start and stop instances manually or have AWS Ops Works Stacks automatically scale the number of instances. You can use time-based automatic scaling with any stack; Linux stacks also can use load-based scaling.
2) In addition to using AWS OpsWorks Stacks to create Amazon L~C2 instances, you can also register instances with a Linux stack that were created outside of AWS Ops Works Stacks. This includes Amazon CC2 instances and instances running on your own hardware. However, they must be running one of the supported Linux distributions. You cannot register Amazon CC2 or on-premises Windows instances.
3) A stack's instances can run either Linux or Windows. A stack can have different Linux versions or distributions on different instances, but you cannot mix Linux and Windows instances.
For more information on Opswork instances, please visit the below url http://docs.aws.a mazon.co m/o psworks/latest/usergu ide/workinginstances-os. html
NEW QUESTION 6
Your application is currently running on Amazon EC2 instances behind a load balancer. Your management has decided to use a Blue/Green deployment strategy. How should you implement this for each deployment?
- A. Set up Amazon Route 53 health checks to fail over from any Amazon EC2 instance that is currently being deployed to.
- B. Using AWS CloudFormation, create a test stack for validating the code, and then deploy the code to each production Amazon EC2 instance.
- C. Create a new load balancer with new Amazon EC2 instances, carry out the deployment, and then switch DNS over to the new load balancer using Amazon Route 53 after testing.
- D. Launch more Amazon EC2 instances to ensure high availability, de-register each Amazon EC2 instance from the load balancer, upgrade it, and test it, and then register it again with the load balancer.
Answer: C
Explanation:
The below diagram shows how this can be done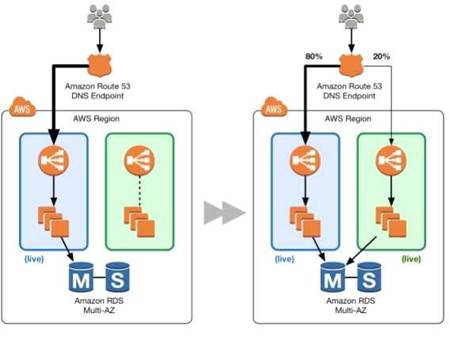
1) First create a new ELB which will be used to point to the new production changes.
2) Use the Weighted Route policy for Route53 to distribute the traffic to the 2 ELB's based on a 80- 20% traffic scenario. This is the normal case, the % can be changed based on the requirement.
3) Finally when all changes have been tested, Route53 can be set to 100% for the new ELB.
Option A is incorrect because this is a failover scenario and cannot be used for Blue green deployments. In Blue Green deployments, you need to have 2 environments running side by side. Option B is incorrect, because you need to a have a production stack with the changes which will run side by side.
Option D is incorrect because this is not a blue green deployment scenario. You cannot control which users will go the new EC2 instances.
For more information on blue green deployments, please refer to the below document link: from AWS
https://dOawsstatic.com/whitepapers/AWS_Blue_Green_Deployments.pdf
NEW QUESTION 7
You have been asked to de-risk deployments at your company. Specifically, the CEO is concerned about outages that occur because of accidental inconsistencies between Staging and Production, which sometimes cause unexpected behaviors in Production even when Staging tests pass. You already use Docker to get high consistency between Staging and Production for the application environment on your EC2 instances. How do you further de-risk the rest of the execution environment, since in AWS, there are many service components you may use beyond EC2 virtual machines?
- A. Develop models of your entire cloud system in CloudFormatio
- B. Use this model in Staging and Production to achieve greater parit
- C. */
- D. Use AWS Config to force the Staging and Production stacks to have configuration parit
- E. Any differences will be detected for you so you are aware of risks.
- F. Use AMIs to ensure the whole machine, including the kernel of the virual machines, is consistent,since Docker uses Linux Container (LXC) technology, and we need to make sure the container environment is consistent.
- G. Use AWS ECS and Docker clusterin
- H. This will make sure that the AMIs and machine sizes are the same across both environments.
Answer: A
Explanation:
After you have your stacks and resources set up, you can reuse your templates to replicate your infrastructure in multiple environments. For example, you can create environments for development, testing, and production so that you can test changes before implementing them into production. To make templates reusable, use the parameters, mappings, and conditions sections so that you can customize your stacks when you create them. For example, for your development environments, you can specify a lower-cost instance type compared to your production environment, but all other configurations and settings remain the same
For more information on Cloudformation best practices please refer to the below link: http://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCIoudFormation/latest/UserGuide/best-practices.html
NEW QUESTION 8
You have an Auto Scaling group of Instances that processes messages from an Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS) queue. The group scales on the size of the queue. Processing Involves calling a third- party web service. The web service is complaining about the number of failed and repeated calls it is receiving from you. You have noticed that when the group scales in, instances are being terminated while they are processing. What cost-effective solution can you use to reduce the number of incomplete process attempts?
- A. Create a new Auto Scaling group with minimum and maximum of 2 and instances running web proxy softwar
- B. Configure the VPC route table to route HTTP traffic to these web proxies.
- C. Modify the application running on the instances to enable termination protection while it processes a task and disable it when the processing is complete.
- D. Increase the minimum and maximum size for the Auto Scalinggroup, and change the scaling policies so they scale less dynamically.
- E. Modify the application running on the instances to put itself into an Auto Scaling Standby state while it processes a task and return itself to InService when the processing is complete.
Answer: D
Explanation:
The following diagram shows the lifecycle of the instances in Autoscaling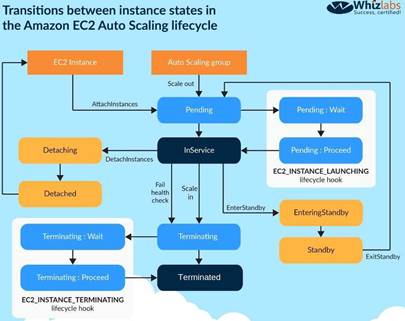
You can put the instances in a standby state, via the application, do the processing and then put the instance back in a state where it can be governed by the
Autoscaling Group.
For more information on the Autoscaling Group Lifecycle please refer to the below link: http://docs.aws.amazon.com/autoscaling/latest/userguide/AutoScaingGroupl_ifecycle.htm I Note: As per AWS documentation.
To control whether an Auto Scaling group can terminate a particular instance when scaling in, use instance protection.
It is termed as Instance protection rather than termination protection when we refer it with "Scaling in process" of ASG.
For more information please view the following link: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/autoscaling/ec2/userguide/as-instance-termination.htmlffinstance- protection-instance
NEW QUESTION 9
An EC2 instance has failed a health check. What will the ELB do?
- A. The ELB will terminate the instance
- B. The ELB stops sending traffic to the instance that failed its health check
- C. The ELB does nothing
- D. The ELB will replace the instance
Answer: B
Explanation:
The AWS Documentation mentions
The load balancer routes requests only to the healthy instances. When the load balancer determines that an instance is unhealthy, it stops routing requests to that instance. The load balancer resumes routing requests to the instance when it has been restored to a healthy state.
For more information on ELB health checks, please refer to the below link: http://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/latest/classic/elb-healthchecks.html
NEW QUESTION 10
You are creating a cloudformation templates which takes in a database password as a parameter. How can you ensure that the password is not visible when anybody tries to describes the stack
- A. Usethe password attribute for the resource
- B. Usethe NoEcho property for the parameter value
- C. Usethe hidden property for the parameter value
- D. Setthe hidden attribute for the Cloudformation resource.
Answer: B
Explanation:
The AWS Documentation mentions
For sensitive parameter values (such as passwords), set the NoEcho property to true. That way, whenever anyone describes your stack, the parameter value is shown as asterisks (*•*").
For more information on Cloudformation parameters, please visit the below URL:
• http://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCIoudFormation/latest/UserGuide/parameters-section- structure.html
NEW QUESTION 11
You are a Devops Engineer for your company. You are responsible for creating Cloudformation templates for your company. There is a requirement to ensure that an S3 bucket is created for all
resources in development for logging purposes. How would you achieve this?
- A. Createseparate Cloudformation templates for Development and production.
- B. Createa parameter in the Cloudformation template and then use the Condition clause inthe template to create an S3 bucket if the parameter has a value of development
- C. Createan S3 bucket from before and then just provide access based on the tag valuementioned in the Cloudformation template
- D. Usethe metadata section in the Cloudformation template to decide on whether tocreate the S3 bucket or not.
Answer: B
Explanation:
The AWS Documentation mentions the following
You might use conditions when you want to reuse a template that can create resources in different contexts, such as a test environment versus a production environment In your template, you can add an CnvironmentType input parameter, which accepts either prod or test as inputs. For the production environment, you might include Amazon CC2 instances with certain capabilities; however, for the test environment, you want to use reduced capabilities to save money. With conditions, you can define which resources are created and how they're configured for each environment type.
For more information on Cloudformation conditions please visit the below url http://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCIoudFormation/latest/UserGuide/cond itions-section- structure.htm I
NEW QUESTION 12
You have a complex system that involves networking, 1AM policies, and multiple, three-tier applications. You are still receiving requirements for the new system, so you don't yet know how many AWS components will be present in the final design. You want to start using AWS CloudFormation to define these AWS resources so that you can automate and version-control your infrastructure. How would you use AWS CloudFormation to provide agile new environments for your customers in a cost-effective, reliable manner?
- A. Manually create one template to encompass all the resources that you need for the system, so you only have a single template to version-control.
- B. Create multiple separate templates for each logical part of the system, create nested stacks in AWS CloudFormation, and maintain several templates to version-contro
- C. •>/
- D. Create multiple separate templates for each logical part of the system, and provide the outputs from one to the next using an Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instance running the SDK forfinergranularity of control.
- E. Manually construct the networking layer using Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) because this does not change often, and then use AWS CloudFormation to define all other ephemeral resources.
Answer: B
Explanation:
As your infrastructure grows, common patterns can emerge in which you declare the same components in each of your templates. You can separate out these common components and create dedicated templates for them. That way, you can mix and match different templates but use nested stacks to create a single, unified stack. Nested stacks are stacks that create other stacks. To create nested stacks, use the AWS::CloudFormation::Stackresource in your template to reference other templates.
For more information on Cloudformation best practises please refer to the below link: http://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCIoudFormation/latest/UserGuide/best-practices.html
NEW QUESTION 13
You are in charge of designing a number of Cloudformation templates for your organization. You are required to make changes to stack resources every now and then based on the requirement. How can you check the impact of the change to resources in a cloudformation stack before deploying changes to the stack?
- A. Thereis no way to control thi
- B. You need to check for the impact beforehand.
- C. UseCloudformation change sets to check for the impact to the changes.
- D. UseCloudformation Stack Policies to check for the impact to the changes.
- E. UseCloudformation Rolling Updates to check for the impact to the changes.
Answer: B
Explanation:
The AWS Documentation mentions
When you need to update a stack, understanding how your changes will affect running resources before you implement them can help you update stacks with confidence. Change sets allow you to preview how proposed changes to a stack might impact your running resources, for example, whether your changes will delete or replace any critical resources, AWS CloudFormation makes the changes to your stack only when you decide to execute the change set, allowing you to decide whether to proceed with your proposed changes or explore other changes by creating another change set. You can create and manage change sets using the AWS
CloudFormation console, AWS CLI, or AWS CloudFormation API.
For more information on Cloudformation change sets, please visit the below url http://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCIoudFormation/latest/UserGuide/using-cfn-updating-stacks-changesets.html
NEW QUESTION 14
An application is currently writing a large number of records to a DynamoDB table in one region. There is a requirement for a secondary application tojust take in the changes to the DynamoDB table every 2 hours and process the updates accordingly. Which of the following is an ideal way to ensure the secondary application can get the relevant changes from the DynamoDB table.
- A. Inserta timestamp for each record and then scan the entire table for the timestamp asper the last 2 hours.
- B. Createanother DynamoDB table with the records modified in the last 2 hours.
- C. UseDynamoDB streams to monitor the changes in the DynamoDB table.
- D. Transferthe records to S3 which were modified in the last 2 hours
Answer: C
Explanation:
The AWS Documentation mentions the following
A DynamoDB stream is an ordered flow of information about changes to items in an Amazon DynamoDB table. When you enable a stream on a table, DynamoDB captures information about every modification to data items in the table.
Whenever an application creates, updates, or deletes items in the table, DynamoDB Streams writes a stream record with the primary key attribute(s) of the items that were modified. Astream record contains information about a data modification to a single item in a DynamoDB table. You can configure the stream so that the stream records capture additional information, such as the "before" and "after" images of modified items.
For more information on DynamoDB streams, please visit the below URL: http://docs.aws.amazon.com/amazondynamodb/latest/developerguide/Streams.html
NEW QUESTION 15
You have created a DynamoDB table for an application that needs to support thousands of users. You need to ensure that each user can only access their own data in a particular table. Many users already have accounts with a third-party identity provider, such as Facebook, Google, or Login with Amazon. How would you implement this requirement?
Choose 2 answers from the options given below.
- A. Createan 1AM User for all users so that they can access the application.
- B. UseWeb identity federation and register your application with a third-partyidentity provider such as Google, Amazon, or Facebook.
- C. Createan 1AM role which has specific access to the DynamoDB table.
- D. Usea third-party identity provider such as Google, Facebook or Amazon so users canbecome an AWS1AM User with access to the application.
Answer: BC
Explanation:
The AWS Documentation mentions the following
With web identity federation, you don't need to create custom sign-in code or manage your own user identities. Instead, users of your app can sign in using a well-known identity provider (IdP) — such as Login with Amazon, Facebook, Google, or any other OpenID Connect (OIDC)-compatible IdP, receive an authentication token, and then exchange that token for temporary security credentials in AWS that map to an 1AM role with permissions to use the resources in your AWS account. Using an IdP helps you keep your AWS account secure, because you don't have to embed and distribute long- term security credentials with your application. For more information on Web Identity federation, please visit the below url http://docs.ws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_roles_providers_oidc.html
NEW QUESTION 16
You have an Autoscaling Group configured to launch EC2 Instances for your application. But you notice that the Autoscaling Group is not launching instances in the right proportion. In fact instances are being launched too fast. What can you do to mitigate this issue? Choose 2 answers from the options given below
- A. Adjust the cooldown period set for the Autoscaling Group
- B. Set a custom metric which monitors a key application functionality forthe scale-in and scale-out process.
- C. Adjust the CPU threshold set for the Autoscaling scale-in and scale-out process.
- D. Adjust the Memory threshold set forthe Autoscaling scale-in and scale-out process.
Answer: AB
Explanation:
The Auto Scaling cooldown period is a configurable setting for your Auto Scaling group that helps to ensure that Auto Scaling doesn't launch or terminate additional instances before the previous scaling activity takes effect.
For more information on the cool down period, please refer to the below link:
• http://docs^ws.a mazon.com/autoscaling/latest/userguide/Cooldown.html
Also it is better to monitor the application based on a key feature and then trigger the scale-in and scale-out feature accordingly. In the question, there is no mention of CPU or memory causing the issue.
NEW QUESTION 17
Which of the following tools is available to send logdatafrom EC2 Instances.
- A. CloudWatch LogsAgent
- B. CloudWatchAgent
- C. Logsconsole.
- D. LogsStream
Answer: A
Explanation:
The AWS Documentation mentions the following
The CloudWatch Logs agent provides an automated way to send log data to Cloud Watch Logs from Amazon L~C2 instances. The agent is comprised of the following components:
A plug-in to the AWS CLI that pushes log data to CloudWatch Logs.
A script (daemon) that initiates the process to push data to CloudWatch Logs.
Acron job that ensures that the daemon is always running. For more information on Cloudwatch logs Agent, please see the below link:
http://docs.aws.a mazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/logs/AgentRefe re nee. htm I
NEW QUESTION 18
You are deciding on a deployment mechanism for your application. Which of the following deployment mechanisms provides the fastest rollback after failure.
- A. Rolling-Immutable
- B. Canary
- C. Rolling-Mutable
- D. Blue/Green
Answer: D
Explanation:
In Blue Green Deployments, you will always have the previous version of your application available.
So anytime there is an issue with a new deployment, you can just quickly switch back to the older version of your application.
For more information on Blue Green Deployments, please refer to the below link: https://docs.cloudfoundry.org/devguide/deploy-apps/blue-green.html
NEW QUESTION 19
You are a Devops Engineer for your company. You have been instructed to create a continuous integrated and continuous delivery model for the application in your organization. Which of the below services could be used for this purpose. Choose 2 answers from the options given below
- A. AWSCodeDeploy
- B. AWSCodePipeline
- C. AWSSQS
- D. AWSIAM
Answer: AB
Explanation:
The AWS Documentation mentions the below
AWS CodeDeploy is a deployment sen/ice that automates application deployments to Amazon EC2 instances or on-premises instances in your own facility.
You can deploy a nearly unlimited variety of application content, such as code, web and configuration files, executables, packages, scripts, multimedia files, and so on. AWS CodeDeploy can deploy application content stored in Amazon S3 buckets, GitHub repositories, or Bitbucket repositories.
For more information on AWS Code Deploy, please visit the below URL:
• http://docs.aws.amazon.com/codedeploy/latest/userguide/welcome.html
AWS CodePipeline is a continuous delivery service you can use to model, visualize, and automate the
steps required to release your software. You can quickly model and configure the different stages of a software release process. AWS CodePipeline automates the steps required to release your software changes continuously. For more information on AWS Code Pipeline, please visit the below URL:
• http://docs.aws.amazon.com/codepipeline/latest/userguide/welcome.html
NEW QUESTION 20
You have a web application running on six Amazon EC2 instances, consuming about 45% of resources on each instance. You are using auto-scaling to make sure that six instances are running at all times. The number of requests this application processes is consistent and does not experience spikes. The application is critical to your business and you want high availability at all times. You want the load to be distributed evenly between all instances. You also want to use the same Amazon Machine Image (AMI) for all instances. Which of the following architectural choices should you make?
- A. Deploy6 EC2 instances in one availability zone and use Amazon Elastic Load Balancer.
- B. Deploy3 EC2 instances in one region and 3 in another region and use Amazon ElasticLoad Balancer.
- C. Deploy3 EC2 instances in one availability zone and 3 in another availability zone anduse Amazon Elastic Load Balancer.
- D. Deploy2 EC2 instances in three regions and use Amazon Elastic Load Balancer.
Answer: C
Explanation:
Option A is automatically incorrect because remember that the question asks for high availability. For option A, if the A2 goes down then the entire application fails.
For Option B and D, the CLB is designed to only run in one region in aws and not across multiple regions. So these options are wrong.
The right option is C.
The below example shows an Elastic Loadbalancer connected to 2 EC2 instances connected via Auto Scaling. This is an example of an elastic and scalable web tier.
By scalable we mean that the Auto scaling process will increase or decrease the number of CC2 instances as required.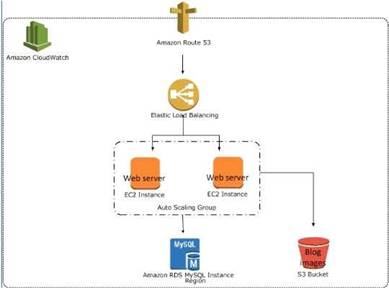
For more information on best practices for AWS Cloud applications, please visit the below URL:
• https://d03wsstatic.com/whitepapers/AWS_Cloud_Best_Practices.pdf
NEW QUESTION 21
You have a number of Cloudformation stacks in your IT organization. Which of the following commands will help see all the cloudformation stacks which have a completed status?
- A. describe-stacks
- B. list-stacks
- C. stacks-complete
- D. list-templates
Answer: B
Explanation:
The following is the description of the list-stacks command
Returns the summary information for stacks whose status matches the specified StackStatusFilter.
Summary information for stacks that have been deleted is kept for 90 days after the stack is deleted. If no stack-status-filter is specified, summary information for all stacks is returned (including existing stacks and stacks that have been deleted).
For more information on the list-stacks command please visit the below link http://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/reference/cloudformation/list-stacks. html
NEW QUESTION 22
Your public website uses a load balancer and an Auto Scalinggroup in a virtual private cloud. Your chief security officer has asked you to set up a monitoring system that quickly detects and alerts your team when a large sudden traffic increase occurs. How should you set this up?
- A. Setup an Amazon CloudWatch alarm for the Elastic Load Balancing Networkln metricand then use Amazon SNS to alert your team.
- B. Usean Amazon EMR job to run every thirty minutes, analyze the Elastic LoadBalancing access logs in a batch manner to detect a sharp increase in trafficand then use the Amazon Simple Email Service to alert your team.
- C. Usean Amazon EMR job to run every thirty minutes analyze the CloudWatch logs fromyour application Amazon EC2 instances in a batch manner to detect a sharpincrease in traffic and then use the Amazon SNS SMS notification to alert yourteam
- D. Setup an Amazon CloudWatch alarm for the Amazon EC2 Networkln metric for the AutoScaling group and then use Amazon SNS to alert your team.
- E. Setup a cron job to actively monitor the AWS CloudTrail logs for increased trafficand use Amazon SNS to alert your team.
Answer: D
Explanation:
The below snapshot from the AWS documentation gives details on the Networkln metric
NEW QUESTION 23
You work for a startup that has developed a new photo-sharing application for mobile devices. Over recent months your application has increased in popularity; this has resulted in a decrease in the performance of the application clue to the increased load. Your application has a two-tier architecture that is composed of an Auto Scaling PHP application tier and a MySQL RDS instance initially deployed with AWS Cloud Formation. Your Auto Scaling group has a min value of 4 and a max value of 8. The desired capacity is now at 8 because of the high CPU utilization of the instances. After some analysis, you are confident that the performance issues stem from a constraint in CPU capacity, although memory utilization remains low. You therefore decide to move from the general-purpose M3 instances to the compute-optimized C3 instances. How would you deploy this change while minimizing any interruption to your end users?
- A. Sign into the AWS Management Console, copy the old launch configuration, and create a new launch configuration that specifies the C3 instance
- B. Update the Auto Scalinggroup with the new launch configuratio
- C. Auto Scaling will then update the instance type of all running instances.
- D. Sign into the AWS Management Console, and update the existing launch configuration with the new C3 instance typ
- E. Add an UpdatePolicy attribute to your Auto Scaling group that specifies AutoScalingRollingUpdate.
- F. Update the launch configuration specified in the AWS CloudFormation template with the new C3 instance typ
- G. Run a stack update with the new templat
- H. Auto Scaling will then update the instances with the new instance type.
- I. Update the launch configuration specified in the AWS CloudFormation template with the new C3instance typ
- J. Also add an UpdatePolicy attribute to your Auto Scalinggroup that specifies AutoScalingRollingUpdat
- K. Run a stack update with the new template.
Answer: D
Explanation:
The AWS::AutoScaling::AutoScalingGroup resource supports an UpdatePoIicy attribute. This is used to define how an Auto Scalinggroup resource is updated when an update to the Cloud Formation stack occurs. A common approach to updating an Auto Scaling group is to perform a rolling update, which is done by specifying the AutoScalingRollingUpdate policy. This retains the same Auto Scaling group and replaces old instances with new ones, according to the parameters specified. For more information on rolling updates, please visit the below link:
• https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/knowledge-center/auto-scaling-group-rolling- updates/
NEW QUESTION 24
......
Recommend!! Get the Full DOP-C01 dumps in VCE and PDF From Downloadfreepdf.net, Welcome to Download: https://www.downloadfreepdf.net/DOP-C01-pdf-download.html (New 116 Q&As Version)
