1Z0-821 Exam
Top Tips Of Renewal 1Z0-821 Samples

Exam Code: 1Z0-821 (Practice Exam Latest Test Questions VCE PDF)
Exam Name: Oracle Solaris 11 System Administrator
Certification Provider: Oracle
Free Today! Guaranteed Training- Pass 1Z0-821 Exam.
Check 1Z0-821 free dumps before getting the full version:
NEW QUESTION 1
What is the result of executing the following command? svcs -d svc:/network/ssh:default
- A. disables the svc:/network/ssh:default service
- B. displays the services that svc: /network/ssh:default is dependent on
- C. displays the services that are dependent on the svc: /network/ssh:default service
- D. deletes the svc: /network/ssh:default service
Answer: B
Explanation:
The svcs command displays information about service instances as recorded in the service configuration repository.
-d Lists the services or service instances upon which the given service instances depend.
NEW QUESTION 2
You have installed the SMF notification framework to monitor services. Which command is used to set up the notifications for a particular service?
- A. svccfg
- B. svcadm
- C. setnotify
- D. smtp-notify
Answer: A
Explanation:
How to Set Up Email Notification of SMF Transition Events
This procedure causes the system to generate an email notification each time one of the services or a selected service has a change in state. You can choose to use either SMTP or SNMP. Normally, you would only select SNMP if you already have SNMP configured for some other reason.
By default, SNMP traps are sent on maintenance transitions. If you use SNMP for monitoring, you can configure additional traps for other state transitions.
1. Become an administrator or assume a role that includes the Service Management rights profile.'
2. Set notification parameters. Example 1:
The following command creates a notification that sends email when transactions go into the maintenance state.
# /usr/sbin/svccfg setnotify -g maintenance mailto:sysadmins@example.com
Example 2:
The following command creates a notification that sends email when the switch service goes into the online state.
# /usr/sbin/svccfg -s svc:/system/name-service/switch:default setnotify to-online \ mailto:sysadmins@example.com
Note: The svccfg command manipulates data in the service configuration repository. svccfg can be invoked interactively, with an individual subcommand, or by specifying a command file that contains a series of subcommands.
Changes made to an existing service in the repository typically do not take effect for that service until the next time the service instance is refreshed.
NEW QUESTION 3
You are logged in as root to a newly installed Solaris 11 system. You issue the command useradd -d, and then examine the /usr/sadm/defadduser file. This file includes the entry defshell=/bin/sh. Which shell will now be the default for the next account created?
- A. bash shell
- B. C shell
- C. korn shod
- D. bourne shell
Answer: A
Explanation:
Oracle Solaris 11 introduces user environment and command-line argument changes that include the following:
* Shell changes - The default shell, /bin/sh, is now linked to ksh93. The default user shell is the Bourne-again (bash) shell.
* The legacy Bourne shell is available as /usr/sunos/bin/sh.
* The legacy ksh88 is available as /usr/sunos/bin/ksh from the shell/ksh88 package.
* Korn shell compatibility information is available in /usr/share/doc/ksh/COMPATIBILITY.
NEW QUESTION 4
The interface net3 should be operating, but is not. Command:
Which command should you enter next?
- A. ipadm create-ip
- B. ipadm enable-if
- C. ipadm show-if
- D. ipadm up-addr
Answer: B
Explanation:
Enable-if -t interface
Enables the given interface by reading the configuration from the persistent store. All the persistent interface properties, if any, are applied and all the persistent addresses, if any, on the given interface will be enabled.
-t, --temporary
Specifies that the enable is temporary and changes apply only to the active configuration.
NEW QUESTION 5
Which option displays the result of running the zfs list command?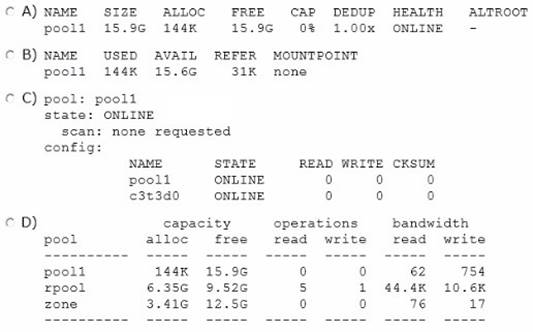
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
Answer: B
Explanation:
The zfs list command provides an extensible mechanism for viewing and querying dataset information.
You can list basic dataset information by using the zfs list command with no options. This command displays the names of all datasets on the system and the values of their used, available, referenced, and mountpoint properties. For more information about these properties, see Introducing ZFS Properties.
For example:
# zfs list
NAME USED AVAIL REFER MOUNTPOINT
pool 476K 16.5G 21K /pool
pool/clone 18K 16.5G 18K /pool/clone pool/home 296K 16.5G 19K /pool/home
pool/home/marks 277K 16.5G 277K /pool/home/marks pool/home/marks@snap 0 - 277K -
pool/test 18K 16.5G 18K /test
NEW QUESTION 6
Identify three differences between the shutdown and init commands.
- A. Only shutdown broadcasts a final shutdown warning to all logged-in users.
- B. init does not terminate all services normall
- C. The shutdown command performs a cleaner shutdown of all services.
- D. The shutdown command can only bring the system to the single-user mileston
- E. The init command must be used to shut the system down to run level 0.
- F. Only shutdown sends a shutdown message to any systems that are mounting resources from the system that is being shut down.
- G. The shutdown command will shut the system down and turn off power; init will only shut the system down.
Answer: ABE
NEW QUESTION 7
You need to set up a local package repository to serve 75 client systems. Multiple clients will being the package repository concurrently and you need to ensure that the local repository performs very well under this heavy load, especially during package intensive operations.
Which option would ensure the best performance of the repository during package-
intensive rations by multiple clients?
- A. Set up multipathing on the package repository server to distribute the network load multiple network interfaces.
- B. Deploy a second instance of the package repository server to run as a read writable mirror.
- C. Deploy a second instance of the package repository server to run as a read-only mirror.
- D. Deploy a second instance of the package repository server to run as a clone of the primary repository server.
- E. Deploy a package repository locally on each client.
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 8
Which statement is correct about shudown and init commands?
- A. shutdown broadcasts one or more periodic shutdown warning messages to all logged-in users whereas init issues none.
- B. The shutdown command performs a clean shutdown of all services whereas init does not.
- C. The shutdown command brings the system to the single-user milestone by defaul
- D. The init command must be used to shut the system down to run level 0.
- E. The shutdown command accepts SMF milestones, init stages, or run levels as arguments whereas init accepts only init stages or run levels as arguments.
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 9
The core dump configuration in your non global zone is
A user is running a process in a non-global zone (testzone) and the process crashes. The process information is:
user126632618017:46:42pts/20:00/usr/bin/bash
When the user's process crashes in testzone, a non-global zone, where will the core dump be saved?
- A. The file will be stored in the non-global zone's directory:/var/core/pprocess/core.hash.2663.
- B. The file will be saved in the global zone's directory: /var/core/core.bash.2663.
- C. A core file cannot be generated in a non-global zone because it shares the kernel with the global zone.
- D. The file will be stored in the global zone's directory: /var/core/pprocess/core.bash.2663.
- E. The file will be saved in non-global zone’s directory: /var/core/core.bash.2663
Answer: E
Explanation:
The line
init core file pattern: /var/core/core.%f.%p
will be used for the non-global process to determine the destination of the dump file.
Note: When a process is dumping core, up to three core files can be produced: one in the per-process location, one in the system-wide global location, and, if the process was running in a local (non-global) zone, one in the global location for the zone in which that process was running.
NEW QUESTION 10
You display the IP interface information with ipmpstat -i.
Which two characteristics are indicated by characters that may be included in the FLAGS column?
- A. default route
- B. IP forwarding enabled IS
- C. allocated to global zone
- D. unusable due to being inactive
- E. nominated to send/receive IPv4 multicast for its IPMP group
Answer: DE
Explanation:
FLAGS
Indicates the status of each underlying interface, which can be one or any combination of the following:
(D) d indicates that the interface is down and therefore unusable.
(E) M indicates that the interface is designated by the system to send and receive IPv6 multicast traffic for the IPMP group.
Note:
i indicates that the INACTIVE flag is set for the interface. Therefore, the interface is not used to send or receive data traffic.
s indicates that the interface is configured to be a standby interface.
m indicates that the interface is designated by the system to send and receive IPv4 multicast traffic for the IPMP group.
b indicates that the interface is designated by the system to receive broadcast traffic for the IPMP group.
h indicates that the interface shares a duplicate physical hardware address with another interface and has been taken offline. The h flag indicates that the interface is unusable.
NEW QUESTION 11
The storage pool configuration on your server is: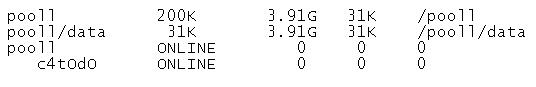
You back up the /pool1/data file system, creating a snapshot and copying that snapshot to tape (/dev/rmt/0). You perform a full backup on Sunday night and Incremental backups on Monday through Saturday night at 11:00 pm. Each incremental backup will copy only the data that has been modified since the Sunday backup was started.
On Thursday, at 10:00 am, you had a disk failure. You replaced the disk drive (c4t0d0). You created pool (pool1) on that disk.
Which option would you select to restore the data in the /pool1/data file system?
- A. zfs create pool1/dataLoad the Monday tape and enter:zfs recv pool1/data </dev/rmt/0Load the Wednesday tape and enter:zfs recv –F pool1/data < /dev/rmt/0
- B. Load the Sunday tape and restore the Sunday snapshot:zfs recv pooll/data </dev/rmt/0zfs rollback pool1/data@monLoad the Wednesday tape and restore the Wednesday snapshot:zfs recv –i pooll/data < /dev/rmt/0zfs rollback pool1/data@wed
- C. zfs create pooll/dataLoad the Wednesday tape and enter:zfs recv -F pool1/data </dev/rmt/0
- D. Load the Sunday tape and enter:zfs recv pool1/data < /dev/rmt/0Load the Wednesday tape and enter:* commands missing*
Answer: D
Explanation:
First the full backup must be restored. This would be the Sunday backup.
Then the last incremental backup must be restored. This would be the Wednesday backup. Before restoring the Wednesday incremental file system snapshot, the most recent snapshot must first be rolled back.
By exclusion D) would be best answer even though it is incomplete.
NEW QUESTION 12
Which files must be edited in order to set up logging of all failed login attempts?
- A. /etc/default/login, /var/adm/loginlog, /etc/syslog.conf
- B. /etc/default/login, /var/adm/authlog, /etc/syslog.conf
- C. /var/adm/loginlog, /var/adm/authlog, /etc/syslog.conf
- D. /etc/default/login, /var/adm/authlog, /var/adm/loginlog
Answer: B
Explanation:
This procedure captures in a syslog file all failed login attempts.
1. Set up the /etc/default/login file with the desired values for SYSLOG and SYSLOG_FAILED_LOGINS
Edit the /etc/default/login file to change the entry. Make sure that SYSLOG=YES is uncommented.
2. Create a file with the correct permissions to hold the logging information. Create the authlog file in the /var/adm directory.
3. Edit the syslog.conf file to log failed password attempts. Send the failures to the authlog file.
NEW QUESTION 13
Before booting test zone a non-global zone, you want to connect to the zone’s console so that you can watch the boot process.
Choose the command used to connect to testzone’s console.
- A. zoneadm -C testzone
- B. zoneadm -console testzone
- C. zlogin - z testzone console
- D. zlogin - z testzone - C
- E. zlogin -C testzone
- F. zoneadm - testzone - c
Answer: E
Explanation:
The following options are supported:
C
Connects to the zone console. Connects to the zone console.
Note:
After you install a zone, you must log in to the zone to complete its application environment. You might log in to the zone to perform administrative tasks as well. Unless the -C option is used to connect to the zone console, logging in to a zone
using zlogin starts a new task. A task cannot span two zones
NEW QUESTION 14
You want to deploy Oracle Solaris 11 with the Automated Installer (AI). You need to make sure that your server and network meet the requirements for using AI.
Identify two requirements for using AI.
- A. You should set up DHC
- B. The DHCP server and AI install server can be the same machine or two different machines.
- C. You can create only one manifest per install servic
- D. If you need more than one manifest, you should create multiple install services.
- E. The minimum requirement to operate as an AI install server is 1 GB of memory.
- F. If two client machines have different architectures and need to be installed with the same version of the Oracle Solaris 11 OS, then you should create two AI manifests and a single install service.
Answer: AD
Explanation:
A: An automated installation of a client over the network consists of the following high-level steps:
Step 1. The client system boots over the network and gets its network configuration and the location of the install server from the DHCP server.
Step 2: The install server provides a boot image to the client. Etc.
D: If two client machines need to be installed with the same version of the Oracle Solaris 11 OS but need to be installed differently in other ways, then create two AI manifests for the AI install service. The different AI manifests can specify different packages to install or a different slice as the install target, for example.
NEW QUESTION 15
A change in your company’s security policy now requires an audit trial of all administrators assuming the sysadm role, capturing:
There are two command necessary to accomplish this change. One is a rolemod command. What is the other?
- A. auditconfig set policy=argv
- B. auditconfig -setpolicy +argv
- C. auditconfig -setflags lo, ex sysadm
- D. auditconfig set flags=lo, ex sysadm
Answer: B
Explanation:
Audit Significant Events in Addition to Login/Logout (see step 2 below)
Use this procedure to audit administrative commands, attempts to invade the system, and other significant events as specified by your site security policy.
For all users and roles, add the AUE_PFEXEC audit event to their preselection mask.
# usermod -K audit_flags=lo, ps:no username
# rolemod -K audit_flags=lo, ps:no rolename
# auditconfig -setpolicy +argv
3- Record the environment in which audited commands are executed.
# auditconfig -setpolicy +arge
Note: [-t] -setpolicy [+|-]policy_flag[, policy_flag ...]
Set the kernel audit policy. A policy policy_flag is literal strings that denotes an audit policy. A prefix of + adds the policies specified to the current audit policies. A prefix of - removes the policies specified from the current audit policies. No policies can be set from a local zone unless the perzone policy is first set from the global zone.
NEW QUESTION 16
On server A, you enter the following command to add a static route to serverA route -p add
-host 192.168.1.101 192.168.1.101 -static
What is the purpose of this command?
- A. to temporarily bypass IP Filter rules
- B. to specify an IPMP target IP address to in.mpathd
- C. to specify routing to an adjacent network when in.rdisc is not used
- D. to specify routing to an adjacent network when in.routed is not used
- E. to ensure the IP address for serverB is not flushed from the ARP cache
- F. to optimize link aggregation using a direct connection between two systems
Answer: B
Explanation:
Note: # route -p add -host destination-IP gateway-IP -static
where destination-IP and gateway-IP are IPv4 addresses of the host to be used as a target.
For example, you would type the following to specify the target system 192.168.10.137, which is on the same subnet as the interfaces in IPMP group itops0:
$ route -p add -host 192.168.10.137 192.168.10.137 -static
This new route will be automatically configured every time the system is restarted. If you
want to define only a temporary route to a target system for probe-based failure detection, then do not use the -p option.
NEW QUESTION 17
The core dump configuration for your system is:
A user is running a process in the global zone and the process crashes. The process information is:
User1 2663 2618 0 17:46:42 pts/2 0:00 /usr/bin/bash
The server host name is: zeus
What will the per-process core file be named?
- A. core.bash.2663.global
- B. core.bash.2663.zeus
- C. /var/core/core.bash.2663
- D. /var/core/core.bash.2663.global
Answer: C
Explanation:
Note the first line:
global core file pattern: /globalcore/core.%f.%p
The program name is bash The runtime process ID is 2663
Note: By default, the global core dump is disabled. You need to use the coreadm command with the -e global option to enable it. The -g option causes the command to append the program name(%f) and the runtime process ID (%p) to the core file name.
NEW QUESTION 18
You are planning group names for a new system. You decide to use a numbering convention that includes the year and month the project began, to form the group number and name for work associated with that project.
So, for example, a project targeted to begin in January, 2013 would have the number (name):
201301(Pr20l301)
What are the two problems with your plan?
- A. Group names may not contain a numeric character
- B. Group names may be no longer than 7 characters.
- C. Group numbers should not be larger than 60000.
- D. Group names should be all lowercase.
Answer: CD
Explanation:
C: The Group ID (GID) field contains the group's numerical ID. GIDs can be assigned whole numbers between 100 and 60000.
D: Group names contain only lowercase characters and numbers.
NEW QUESTION 19
View the exhibit to inspect the file system configuration on your server.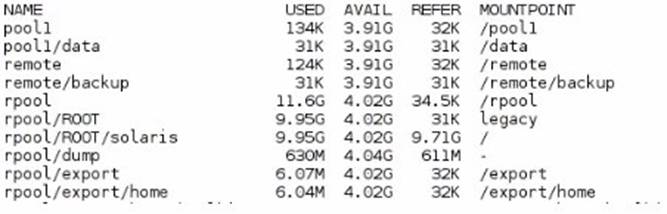
View the Exhibit to inspect the file system configuration on your server.
Your department's backup policy is to perform a full backup to a remote system disk on Saturday.
On Sunday through Friday, you are to perform a differential backup to the same remote system disk:
Following your company policy, which option describes a valid procedure for backing up the /data file system to a remote disk named /remote/backup?
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 20
Identify the Automated Installer’s (AI) equivalent to jumpStart’s finish scripts and sysidcfg files.
- A. Manifest files
- B. SMF system configuration profile files
- C. Installadm create - client
- D. IPS software package repository
- E. installadm create-service
- F. svccfg - s application/pkg/server setprop sysidcfg
Answer: B
Explanation:
Comparing sysidcfg File Keywords to System Configuration Profile Directives
The following table compares sysidcfg file keywords with example AI system configuration profile specifications.
sysidcfg File Keyword
System Configuration Profile Directives Etc.
NEW QUESTION 21
The default publisher on your system is:
You want to update the Oracle Solaris 11 environment on your system, but you are not able to connect this system to the Internet to access the default Oracle repository. A repository has been created on your local network and is named http://server1.example.com.
Which command would you choose to connect your system to the local repository?
- A. pkg publisher to specify the new publisher
- B. pkg set-publisher to set the stickiness on the http://server1.example.com publisher and unset stickiness for http://pkg.oracle.com/solaris/release
- C. pkg add-publisher to add the new publisher
- D. pkg set-publisher to set the origin for the publisher
Answer: D
Explanation:
Solaris 11 Express makes it pretty easy to set up a local copy of the repository.
A common reason folks need access to a local repository is because their system is not connected to the Internet.
Tthe pkg set-publisher command can be used to for example add a publisher or to enable or disable a publisher.
Note: Example Adding a Publisher
Use the -g option to specify the publisher origin URI.
# pkg set-publisher -g http://pkg.example.com/release example.com Example Specifying the Preferred Publisher
Use the -P option to specify a publisher as the preferred publisher. The specified publisher moves to the top of the search order. You can specify the -P option when you add a publisher or you can modify an existing publisher.
# pkg set-publisher -P example.com Example Enabling or Disabling a Publisher
Use the -d option to disable a publisher. The preferred publisher cannot be disabled. A disabled publisher is not used in package operations such as list and install. You can modify the properties of a disabled publishers.
Use the -e option to enable a publisher.
# pkg set-publisher -d example2.com
NEW QUESTION 22
United States of America export laws include restrictions on cryptography.
Identify the two methods with which these restrictions are accommodated in the Oracle Solaris 11 Cryptographic Framework.
- A. Corporations must utilize signed X.509 v3 certificates.
- B. A third-party provider object must be signed with a certificate issued by Oracle.
- C. Loadable kernel software modules must register using the Cryptographic Framework SPI.
- D. Third-party providers must utilize X.509 v3 certificates signed by trusted Root Certification Authorities.
- E. Systems destined for embargoed countries utilize loadable kernel software modules that restrict encryption to 64 bit keys.
Answer: BC
Explanation:
B: Binary Signatures for Third-Party Software
The elfsign command provides a means to sign providers to be used with the Oracle Solaris Cryptographic Framework. Typically, this command is run by the developer of a provider.
The elfsign command has subcommands to request a certificate from Sun and to sign binaries. Another subcommand verifies the signature. Unsigned binaries cannot be used by the Oracle Solaris Cryptographic Framework. To sign one or more providers requires the certificate from Sun and the private key that was used to request the certificate.
C: Export law in the United States requires that the use of open cryptographic interfaces be restricted. The Oracle Solaris Cryptographic Framework satisfies the current law by requiring that kernel cryptographic providers and PKCS #11 cryptographic providers be signed.
NEW QUESTION 23
......
P.S. Downloadfreepdf.net now are offering 100% pass ensure 1Z0-821 dumps! All 1Z0-821 exam questions have been updated with correct answers: https://www.downloadfreepdf.net/1Z0-821-pdf-download.html (243 New Questions)
