1Z0-821 Exam
How Many Questions Of 1Z0-821 Questions Pool

Passleader 1Z0-821 Questions are updated and all 1Z0-821 answers are verified by experts. Once you have completely prepared with our 1Z0-821 exam prep kits you will be ready for the real 1Z0-821 exam without a problem. We have Latest Oracle 1Z0-821 dumps study guide. PASSED 1Z0-821 First attempt! Here What I Did.
Check 1Z0-821 free dumps before getting the full version:
NEW QUESTION 1
Which network protocol is responsible for routing packets from one network to another?
- A. TCP
- B. UDP
- C. IP
- D. ICMP
- E. Ethernet
Answer: C
Explanation:
The Internet Protocol (IP) is the principal communications protocol in the Internet protocol suite for relaying datagrams across network boundaries. Its routing function enables internetworking, and essentially establishes the Internet.
NEW QUESTION 2
You want to display the IP address assignments of the network interfaces. Which command should you use?
- A. ipadm show-if
- B. ipadm show-addr
- C. ipadm show-prop
- D. ipadm show-addrprop
Answer: B
Explanation:
'ipadm show-addr' displays all the configured addresses on the system. Example:
# ipadm show-addr
ADDROBJ TYPE STATE ADDR
lo0/v4 static ok 127.0.0.1/8 lo0/v6 static ok ::1/128
NEW QUESTION 3
Select the packet type that identifies members of the group and sends information to all the network interfaces in that group.
- A. Unicast
- B. Multicast
- C. Broadcast
- D. Bayesian
- E. Quality of Service Priority
Answer: B
Explanation:
IPv6 defines three address types: unicast
Identifies an interface of an individual node.
multicast
Identifies a group of interfaces, usually on different nodes. Packets that are sent to the multicast address go to all members of the multicast group.
anycast
Identifies a group of interfaces, usually on different nodes. Packets that are sent to the anycast address go to the anycast group member node that is physically closest to the sender.
NEW QUESTION 4
You are setting up a local IPS package repository on your Oracle Solaris11 server: solaris.example.com.
You want to point the existing local IPS publisher to the new local IPS repository located in
/repo.
These are the stops that you have followed:
1. Download and rsync the contents of the Oracle Solaris11 repository ISO image to the
/repo directory.
2. Configure the repository server service properties. The svcprop command display, the IPS related properties:
pkg/inst_root astring/repo pkg/readonly Boolean true
The 1s command displays the contents of the /repo directory:
#ls/repo
Pkg5.repository publisher
The svcs publisher command shows the svc: /application/pkg/server: default service is online.
The pkg publisher command shows the svc: /application/pkg/server: default service is online.
The pkg publisher command still displays: PUBLISHERTYPESTATUSURI
solarisoriginonlinehttp://pkg.oracle.com/solaris/release/
Which steps needs to be performed to set the local IPS publisher to the local IPS repository/repo?
- A. Issue the pkgrepo refresh -s command to refresh the repository.
- B. Restart the svc:/application/pkg/server:default service.
- C. pkg set-publisher command to set the new repository location.
- D. Issue the pkgrepo rebuild command to rebuild the repository.
- E. Issue the pkgrepo set command to set the new repository location.
Answer: C
Explanation:
Set the Publisher Origin To the File Repository URI
To enable client systems to get packages from your local file repository, you need to reset the origin for the solaris publisher. Execute the following command on each client:
Example:
# pkg set-publisher -G '*' -M '*' -g /net/host1/export/repoSolaris11/ solaris
NEW QUESTION 5
You wish to troubleshoot some issues that you are having on the system. You want to monitor the /var/adm/messages file in real time. Which command would you use to do this?
- A. head
- B. tail
- C. cat
- D. file
- E. test
Answer: B
Explanation:
tail is a program on Unix and Unix-like systems used to display the last few lines of a text file or piped data.
By default, tail will print the last 10 lines of its input to the standard output. With command line options the number of lines printed and the printing units (lines, blocks or bytes) may be changed. The following example shows the last 20 lines of filename:
tail -n 20 filename
NEW QUESTION 6
You wish to edit your crontab file that is located in /var/spool/cron/crontab. What command must you enter to edit this file?
- A. crontab –e
- B. crontab –e /var/spool/cron/crontab
- C. crontab –r
- D. crontab –e /etc/default/cron
Answer: A
Explanation:
The main tool for setting up cron jobs is the crontab command, though this is not available on every Unix variant. Typically under Solaris or Linux one would create a new crontab or edit an existing one, using the command;
crontab -e
Use the ls -l command to verify the contents of the/var/spool/cron/crontabs file.
NEW QUESTION 7
Which two options describe how to override the default boot behavior of an Oracle Solaris 11 SPARC system to boot the system to the single-user milestone?
- A. from the ok prompt, issue this command: boot -m milestone=single-user
- B. From the ok prompt, issue this command: boot -m milestone/single-user
- C. From the ok prompt, issue this command: boot -milestone=single-user
- D. From the ok promp
- E. issue this command:boot -s
- F. From from the ok prompt, issue this command:boot -m milestone=s
Answer: AD
Explanation:
By default, Solaris will boot to the pseudo milestone “all” and start all services. This behaviour can be changed at boot time using either “-s” to reach single-user, or the new SMF option “-m milestone=XXX” (see kernel(1M) for a list of the bootable milestones) to select an explicit milestone.
Note: boot -s is the same as: boot -m milestone=single-user
with the difference being that the former is a lot less to type and is what most SysAdmins will be familiar with.
NEW QUESTION 8
You are installing the Solaris 11 Operation System by using the Text Installer. A panel
prompts you to create a root password and a user account.
Which four describe your options for completing this panel of the Installation?
- A. Creating a user account is optional.
- B. The root password must be set and cannot be blank.
- C. The root password can be left blank.
- D. If you provide a username, that user is assigned the root role.
- E. If you provide a username, that user is given root privileges.
- F. If you provide a username, root is an account rather than a role and is set to expire immediately.
- G. If you do not provide a username, root is an account rather than a role and is set to expire immediately.
Answer: ABDG
Explanation:
A: You are not required to create a user account. B: You must create a root password.
D: If you create a user account in this panel, you need to provide both the user's password and a root password.
In this case, root will be a role assigned to the user.
G: If you do not create a user account, you still need to provide a root password. In this case, root will be a regular user.
NEW QUESTION 9
You have already generated a 256-bit AES raw key and named the keystore file /mykey. You need to use the key to create an encrypted file system.
Which command should you use to create a ZFS encrypted file system named pool1/encrypt using the /mykey keystore?
- A. zfs create - o encryption = /mykey pool1/encrypt
- B. zfs create - o encryption = 256-ccm - o keysource = raw, file : ///my key pool1/encrypt
- C. zfs create - o encryption = AES keysource = /mykey pool1/encrypt
- D. zfs create - o encryption = on keystore = /mykey pool1/encrypt
Answer: B
Explanation:
Example: Encrypting a ZFS File System by Using a Raw Key
In the following example, an aes-256-ccm encryption key is generated by using the pktool command and is written to a file, /cindykey.file.
# pktool genkey keystore=file outkey=/cindykey.file keytype=aes keylen=256
Then, the /cindykey.file is specified when the tank/home/cindy file system is created.
# zfs create -o encryption=aes-256-ccm -o keysource=raw, file:///cindykey.file tank/home/cindys
NEW QUESTION 10
Your users are experiencing delay issues while using their main application that requires connections to remote hosts. You run the command uptime and get the flowing output:
1:07am up 346 day(s), 12:03, 4 users, load average: 0.02, 0.02, 0.01 Which command will be useful in your next step of troubleshooting?
- A. ipadm
- B. traceroute
- C. dladm
- D. snoop
- E. arp
Answer: B
Explanation:
Test the remote connection with traceroute.
The Internet is a large and complex aggregation of network hardware, connected together by gateways. Tracking the route one's packets follow (or finding the miscreant gateway that's discarding your packets) can be difficult. traceroute utilizes the IP protocol `time to live' field and attempts to elicit an ICMP TIME_EXCEEDED response from each gateway along the path to some host.
This program attempts to trace the route an IP packet would follow to some internet host by launching UDP probe packets with a small ttl (time to live) then listening for an ICMP "time exceeded" reply from a gateway.
NEW QUESTION 11
View the Exhibit.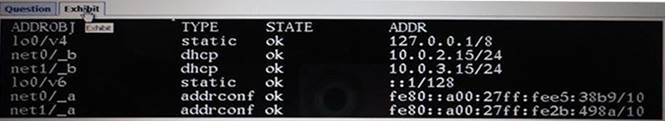
After Installing the OS, you need to verify the network interface information. Which command was used to display the network interface information in the exhibit?
- A. ifconfiq –a
- B. ipadm show-addr
- C. svcs –1 network/physical
- D. netstat –a
Answer: B
Explanation:
'ipadm show-addr' displays all the configured addresses on the system. Example:
# ipadm show-addr
ADDROBJ TYPE STATE ADDR
lo0/v4 static ok 127.0.0.1/8 lo0/v6 static ok ::1/128
NEW QUESTION 12
Which two accurately describe the Solaris IPS repository?
- A. It contains a collection of operating system patches.
- B. It contains a collection of software packages.
- C. All packages within an IPS package repository reside in a catalog.
- D. It is an ISO image of the Solaris installation media.
- E. The packages in a catalog are associated with a specific publisher.
Answer: BE
Explanation:
Image Packaging System (IPS) is a new network based package management system included in Oracle Solaris 11. It provides a framework for complete software lifecycle management such as installation, upgrade and removal of software packages. IPS also enables you to create your own software packages, create and manage package repositories, and mirror existing package repositories.
Oracle Solaris software is distributed in IPS packages. IPS packages are stored in IPS package repositories, which are populated by IPS publishers.
E: The following command displays property information about the local repository.
$ pkgrepo get -s /export/repoSolaris11
SECTION PROPERTY VALUE publisher prefix solaris repository description This\ repository\ serves\ a\ copy\ of\ the\ Oracle\ Solaris\ 11\ Build\ 175b\ Package\ Repository. repository name Oracle\ Solaris\ 11\ Build\ 175b\ Package\ Repository
repository version 4
The value of the publisher prefix specifies that solaris is to be used in the following cases:
When more than one publisher's packages are present and no publisher is specified in the package name in the pkg command
When packages are published to the repository and no publisher is specified.
NEW QUESTION 13
You have been asked to terminate a process that appears to be hung and will not terminate. The process table is shown below:
root 15163 15156 0 12:51:15 pts/3 0:00 hungscript What command will terminate the process?
- A. kill -9 15163
- B. kill -1 15163
- C. kill -15 15163
- D. kill -2 15163
Answer: A
Explanation:
Here we should use SIGTERM to terminate the process. Note:
When no signal is included in the kill command-line syntax, the default signal that is used is
–15 (SIGKILL). Using the –9 signal (SIGTERM) with the kill command ensures that the process terminates promptly. However, the –9 signal should not be used to kill certain processes, such as a database process, or an LDAP server process. The result is that data might be lost.
Tip - When using the kill command to stop a process, first try using the command by itself, without including a signal option. Wait a few minutes to see if the process terminates before
using the kill command with the -9 signal.
NEW QUESTION 14
Examine this command and its output:
$ zfs list -r -t all tank
Name USED AVAIL REFER MOUNTPOINT
tank 2.41G 2.43G 32K /tank
tank/database 2.41G 2.43G 2.41G /tank/database tank/[email protected] 20K - 2.00G –
Next you execute:
# zfs destroy tank/database
Which statement is true about the result of executing this command?
- A. It destroys the tank/database dataset.
- B. It destroys tank/database and all descendant datasets.
- C. It fails because the tank/[email protected] snapshot depends on the tank/database dataset.
- D. It fails because the tank/[email protected] clone depends on the tank/database dataset.
- E. It fails because the tank/database data set is not empty.
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 15
Which three options describe the purpose of the zonep2vchk command?
- A. Used on a Solaris 10 global zone to access the system for problems before migrating that system to a Solaris 10 branded zone.
- B. Used to access a Solaris 10 global zone for problems before migrating that zone to a Solaris 11 global zone
- C. Used to create zonecfg template for a Solaris 10 global zone that that will be migrated to a solaris10 branded zone.
- D. Used to migrate an Oracle Solaris 11 global zone to a non-global zone.
- E. Used to migrate a Solaris 10 global zone to a non-global zone on the same server; the non-global zone can then be migrated to a Solaris 11 server as a Solaris10 branded zone.
Answer: CDE
Explanation:
zonep2vchk
- check a global zone's configuration for physical to virtual migration into non-global zone
The zonep2vchk utility is used to evaluate a global zone's configuration before the process of physical-to-virtual (p2v) migration into a non-global zone.
The p2v process involves archiving a global zone (source), and then installing a non-global zone (target) using that archive
Zonep2vchk serves two functions. First, it can be used to report issues on the source which might prevent a successful p2v migration. Second, it can output a template zonecfg, which can be used to assist in configuring the non-global zone target.
Zonep2vchk can be executed on a Solaris 10 or later global zone. To execute on Solaris 10, copy the zonep2vchkutility to the Solaris 10 source global zone.
When run on Solaris 10, a target release of S11 can be specified, which will check
for p2v into a Solaris 10 Branded zone.
NEW QUESTION 16
View the Exhibit to inspect the boot environment Information displayed within a non global zone on your system.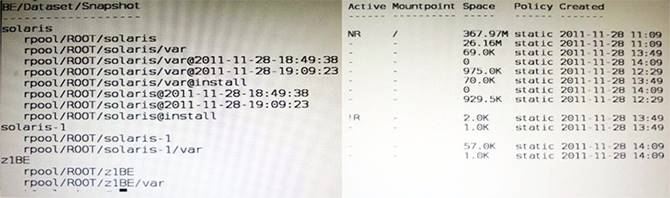
Which two options describe the solaris-1 boot environment?
- A. The solaris-1 boot environment is not bootable.
- B. The solaris-1 boot environment is incomplete.
- C. The solaris-1 boot environment was created automatically when the non global zone was created.
- D. The solaris-1 boot environment was created in the non-global zone using the beadm create command.
- E. The solaris-1 boot environment is associated with a non active global zone boot environment.
Answer: AE
Explanation:
A: The – of the Active Column indicates that this boot environment is inactive, and hence not bootable.
Note: The values for the Active column are as follows: R – Active on reboot.
N – Active now.
NR – Active now and active on reboot. “-” – Inactive.
“!” – Unbootable boot environments in a non-global zone are represented by an exclamation point.
http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E23824_01/html/E21801/unbootable.html#scrolltoc
NEW QUESTION 17
You want to delete the IPv4 address on the interface net3. Which command should you use?
- A. ipadm delete-ip net3/v4
- B. ipadm down-addr net3/v4
- C. ipadm disable-if net3/v4
- D. ipadm delete-vni net3/v4
- E. ipadm delete-addr net3/v4
- F. ipadm deiete-ipv4 ner3/v4
Answer: E
Explanation:
The ipadm delete-addr subcommand removes addresses from interfaces. To remove an address from the IPMP group, type the following command:
# ipadm delete-addr addrobj
The addrobj uses the naming convention inder-interface/user-string.
NEW QUESTION 18
User jack logs in to host solaris and then attempts to log in to host oracle using ssh. He receives the following error message:
The authenticity of host oracle (192.168.1.22) can't be established. RSA key fingerprint is 3B:23:a5:6d:ad:a5:76:83:9c:c3:c4:55:a5:18:98:a6
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)?
Which two are true?
- A. The public host key supplied by solaria is not known to the host oracle.
- B. The error would not occur if the RSA key fingerprint shown in the error message was added to the /etc/ssh/known_hosts file on solaris.
- C. The private host key supplied by oracle is not known to solaris.
- D. If jack answers yes, the RSA public key for the host oracle will be added to the known_hosts file for the user jack.
- E. The public host key supplied by oracle is not known to the host solaris.
Answer: BD
Explanation:
The fingerprints are used to guard against man in the middle attacks. Since ssh logins usually work over the internet (an insecure connection), someone could hijack your connection. When you try to log into yourmachine.com, he could get "in the middle" and return your challenge as if he was yourmachine.com. That way, he could get hold of your login password.
To make this attack harder, ssh stores the fingerprint of the server's public key on the first connection attempt. You will see a prompt like:
The authenticity of host 'eisen (137.43.366.64)' can't be established. RSA key fingerprint is cf:55:30:31:7f:f0:c4:a0:9a:02:1d:1c:41:cf:63:cf. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)
When you enter yes, ssh will add the fingerprint to your known_hosts file. you will see
Code:
Warning: Permanently added 'eisen, 137.43.366.64' (RSA) to the list of known hosts.
The next time you login, ssh will check whether the host key has changed. A changing host key usually indicates a man in the middle attack, and ssh refuses to connect.
NEW QUESTION 19
The following line is from /etc/shadow in a default Solaris 11 Installation:
jack: $5$9JFrt54$7JdwmO.F11Zt/ jFeeOhDmnw93LG7Gwd3Nd/cwCcNWFFg:0:15:30:3::: Which two are true?
- A. Passwords for account jack must be a minimum of 15 characters long.
- B. The password for account jack has expired.
- C. The password for account jack has 5 characters.
- D. A history of 3 prior passwords for the account jack is kept to inhibit password reuse.
- E. The minimum lifetime for a password for account jack is 15 days.
Answer: BE
Explanation:
From the content of the /etc/shadow file we get:
* username: jack
* encrypted password: $5$9JFrt54$7JdwmO.F11Zt/ jFeeOhDmnw93LG7Gwd3Nd/cwCcNWFFg
* Last password change (lastchanged): Days since Jan 1, 1970 that password was last changed: 0
* Minimum: The minimum number of days required between password changes i.e. the number of days left before the user is allowed to change his/her password: 15
Maximum: The maximum number of days the password is valid (after that user is forced to change his/her password): 30 Warn : The number of days before password is to expire that user is warned that his/her password must be changed: 3
* Inactive : The number of days after password expires that account is disabled
* Expire : days since Jan 1, 1970 that account is disabled i.e. an absolute date specifying when the login may no longer be used
NEW QUESTION 20
Your server has a ZFS storage pool that is configured as follows: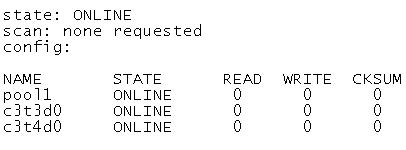
The server has two spate 140-GB disk drives: c3t5d0 c3t6d0 Which command would add redundancy to the pool1 storage pool?
- A. zpool attach pool1 c3t5d0 c3t6d0
- B. zpool attach pool1 c3t3d0 c3c5d0; zpoo1 attach pool1 c3t4d0 c3t6d0
- C. zpool mirror pool1 c3t5d0 c3t6d0
- D. zpool add pool1 mirror c3t5d0 c3t6d0
- E. zpool add raidz pool1 c3t5d0 c3t6d0
Answer: A
Explanation:
You can convert a non-redundant storage pool into a redundant storage pool by using the zpool attach command.
Note: zpool attach [-f] pool device new_device
Attaches new_device to an existing zpool device. The existing device cannot be part of a raidz configuration. If device is not currently part of a mirrored configuration, device automatically transforms into a two-way mirror of device and new_device. If device is part of a two-way mirror, attaching new_device creates a three-way mirror, and so on. In either case, new_device begins to resilver immediately.
NEW QUESTION 21
You are installing the Oracle Solaris 11 Operating System by using the Text Installer. Which two options describe the features associated with the Text Installer?
- A. It can be used to install only SPARC systems.
- B. It installs gnome as the default user environment on a system capable of displaying a graphical environment.
- C. You can choose whether root is a role or user account.
- D. You can do both automatic and manual configuration of the network.
- E. You can select how to configure the remaining network interfaces.
Answer: CD
NEW QUESTION 22
You are going to use the- Automated installer (AI) to install a non global zone named zone1. You have created a custom manifest for the non-global zone and named it zone1manifest
Which command will you use to add this custom manifest to the s11-sparc install service and associate this custom manifest with the non-global zone?
- A. installadm create-profile -n s11-sparc -f /tmp/zone1manifest.xml - c
- B. installadm create-manifest -n s11-sparc -f /tmp/zone1manifest.xml -m
- C. installadm create-client -n s11-sparc -f /tmp/zone1manifest.xml -m zone1manifest -c zonename= “zone1”
- D. installadm create-service - n s11-sparc -f /tmp/zone1manifest.xml -m zone1manifest - c zonename=”zone1”
Answer: B
Explanation:
installadm add-manifest
Associates manifests with a specific install service, thus making the manifests available on the network, independently from creating a service. When publishing a non-default manifest, it is required to associate criteria either via criteria entered on the command line (-c) or via a criteria XML file (-C).
NEW QUESTION 23
......
100% Valid and Newest Version 1Z0-821 Questions & Answers shared by Surepassexam, Get Full Dumps HERE: https://www.surepassexam.com/1Z0-821-exam-dumps.html (New 243 Q&As)
