642-997 Exam
Cisco 642-997 Dumps 2021

It is more faster and easier to pass the 642 997 dumps by using 642 997 dumps. Immediate access to the 642 997 dumps and find the same core area 642 997 dumps with professionally verified answers, then PASS your exam with a high score now.
Check 642-997 free dumps before getting the full version:
NEW QUESTION 1
Which four options are capabilities of the Cisco Nexus 5000 and 5500 Series Switch? (Choose four.)
- A. line rate
- B. managed by a parent switch
- C. lossless 10 Gigabit Ethernet
- D. lossless 100 Gigabit Ethernet
- E. low latency
- F. extremely low latency
- G. hosts a virtual supervisor module
Answer: ACEG
NEW QUESTION 2
Which command ensures that a learned MAC address is stored within NVRAM?
- A. switchport port-security mac-address address [vlan vlan-ID]
- B. switchport port-security
- C. switchport port-security mac-address sticky
- D. feature port-security
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 3
Which statement about implementation of Cisco TrustSec on Cisco Nexus 5546 or 5548 switches are true?
- A. Cisco TrustSec support varies depending on Cisco Nexus 5500 Series Switch model.
- B. The hardware is not able to support MACsec switch-port-level encryption based on IEEE 802.1AE.
- C. The maximum number of RBACL TCAM user configurable entries is 128k.
- D. The SGT Exchange Protocol must use the management (mgmt 0) interface.
Answer: B
Explanation: Reference: https://scadahacker.com/library/Documents/Manuals/Cisco%20-%20TrustSec%20Solution%20Overview.pdf
NEW QUESTION 4
Refer to the exhibit.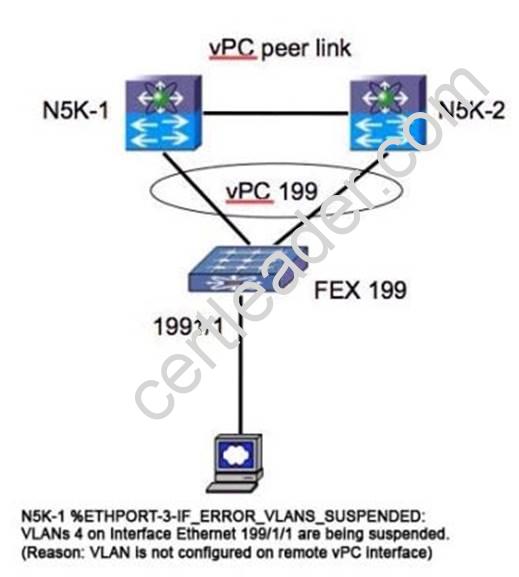
Which corrective action would you take to resolve the problem?
- A. Trunk four VLANs on interface ethernet 199/1/1.
- B. Use the shut and no shut interface ethernet 199/1/1 so that the VLANs come up.
- C. Place interface ethernet 199/1/1 in VLAN 4 in the N5K-2 configuration.
- D. Prune all but four VLANs from vPC 199.
- E. Add VLAN 4 to vPC 199.
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 5
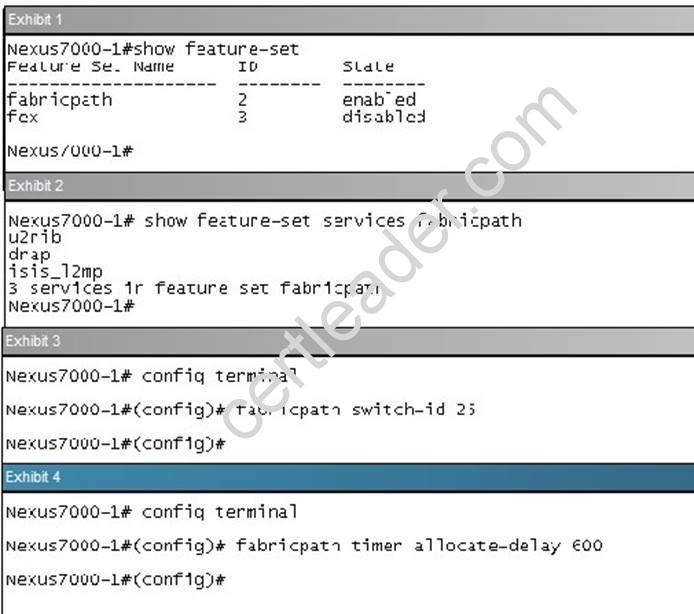
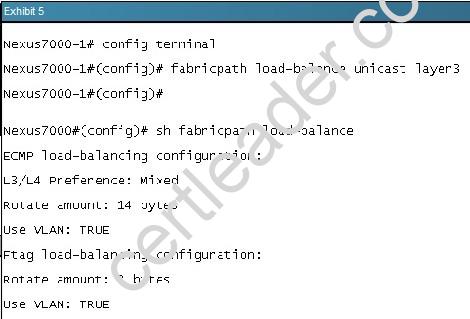
Customer has configured fabricpath allocate-delay to 600. What is the effect of this?
- A. The allocate-delay is the time for FP to go into forwarding state
- B. It specifies the time delay for a transitioned value to be propagated throughout the network
- C. It specifies the time delay for a link bringup to detect conflicts
- D. The allocate-delay is the time delay for a new resource to be propagated throughout the network
Answer: D
Explanation: Specifies the time delay for a new resource to be propagated throughout the network. Reference: http://www.cisco.com/web/techdoc/dc/reference/cli/nxos/commands/fpath/fabricpath_timers.html
Topic 5, Implement Cisco Unified Fabric Network Features and Functionality in a Cisco Data Center Environment
NEW QUESTION 6
Which two types of traffic are carried over a vPC peer link when no failure scenarios are present? (Choose two.)
- A. multicast data traffic
- B. unicast data traffic
- C. broadcast data traffic
- D. vPC keep-alive messages
Answer: AC
NEW QUESTION 7
Which two reasons explain why a server on VLAN 10 is unable to join a multicast stream that originates on VLAN 20? (Choose two.)
- A. IGMP snooping and mrouter are not enabled on VLAN 10.
- B. VLAN 20 has no IGMP snooping querier defined and VLAN 10 has no mrouter.
- C. The mrouter on VLAN 20 does not see the PIM join.
- D. The mrouter must be on VLAN 10 and VLAN 20.
Answer: AC
Explanation: IGMP snooping is a mechanism to constrain multicast traffic to only the ports that have receivers attached. The mechanism adds efficiency because it enables a Layer 2 switch to selectively send out multicast packets on only the ports that need them. Without IGMP snooping, the switch floods the packets on every port. The switch "listens" for the exchange of IGMP messages by the router and the end hosts. In this way, the switch builds an IGMP snooping table that has a list of all the ports that have requested a particular multicast group.
The mrouter port is simply the port from the switch point of view that connects to a multicast router. The presence of at least one mrouter port is absolutely essential for the IGMP snooping operation to work across switches.
All Catalyst platforms have the ability to dynamically learn about the mrouter port. The switches passively listen to either the Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) hellos or the IGMP query messages that a multicast router sends out periodically.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/switches/catalyst-6500-series-switches/68131-cat-multicast-prob.html
NEW QUESTION 8
In OTV, how are the VLANs split when a site has two edge devices?
- A. They are configured manually by user.
- B. They are split in half among each edge device.
- C. They are split as odd and even VLAN IDs on each edge device.
- D. It is not possible to have two edge devices in same site.
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 9
A Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extender is connected to two Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches via a vPC link. After both Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches lose power, only one switch is able to power back up. At this time, the Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extender is not active and the vPC ports are unavailable to the network.
Which action will get the Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extender active when only one Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch is up and active?
- A. Move the line from the failed Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch to the switch that is powered on, so the port channel forms automatically on the switch that is powered on.
- B. Shut down the peer link on the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch that is powered on.
- C. Configure reload restore or auto-recovery reload-delay on the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch that is powered on.
- D. Power off and on the Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extender so that it can detect only one Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch at power up.
Answer: C
Explanation: The vPC consistency check message is sent by the vPC peer link. The vPC consistency check cannot be performed when the peer link is lost. When the vPC peer link is lost, the operational secondary switch suspends all of its vPC member ports while the vPC member ports remain on the operational primary switch. If the vPC member ports on the primary switch flaps afterwards (for example, when the switch or server that connects to the vPC primary switch is reloaded), the ports remain down due to the vPC consistency check and you cannot add or bring up more vPCs. Beginning with Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1), the auto-recovery feature brings up the vPC links when one peer is down. This feature performs two operations:
Beginning with Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1), the auto-recovery feature brings up the vPC links when one peer is down. This feature performs two operations:
•assume the role of the primary switch. The vPC links come up after a configurable period of time if the vPC peer-link and the peer-keepalive fail to become operational within that time. If the peer-link comes up but the peer-keepalive does not come up, both peer switches keep the vPC links down. This feature is similar to the reload restore feature in Cisco NX- OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) and earlier releases. The reload delay period can range from 240 to 3600 seconds. •When you disable vPCs on a secondary vPC switch because of a peer-link failure and then the primary vPC switch fails, the secondary switch reenables the vPCs. In this scenario, the vPC waits for three consecutive keepalive failures before recovering the vPC links.
•When you disable vPCs on a secondary vPC switch because of a peer-link failure and then the primary vPC switch fails, the secondary switch reenables the vPCs. In this scenario, the vPC waits for three consecutive keepalive failures before recovering the vPC links.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/nexus5000/sw/operations/n5k_v pc_ops.html
NEW QUESTION 10
Which zoning security feature locks the zone until the administrator has completed a change?
- A. Commit Lock
- B. Enhanced
- C. Zoning Plus
- D. RBAC
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 11
Which command activates the port security database for VSAN 1 regardless of conflicts?
- A. port-security commit vsan 1
- B. no port-security auto-learn vsan 1
- C. port-security activate vsan 1 force
- D. port-security database vsan 1
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 12
Refer to the exhibit.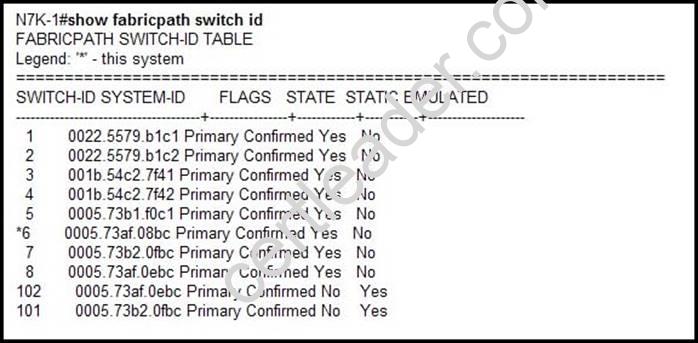
Which three statements about the Cisco Nexus 7000 switch are true? (Choose three.)
- A. An emulated switch ID must be unique when the vPC+ feature is used.
- B. Switches with FabricPath and vPC+ consume two switch IDs.
- C. Emulated switch IDs must be numbered from 1 to 99.
- D. Each switch ID must be unique in the FabricPath topology.
- E. Switch IDs must be configured manually.
Answer: BDE
Explanation: To understand this feature, please refer to the link given below.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/switches/nexus-5000-series-switches/guide_c07-690079.html#wp9000065
NEW QUESTION 13
Which three VDC resources can be constrained with a resource template? (Choose three.)
- A. ACLs
- B. NAT entries
- C. IPv4 routes
- D. IPv6 routes
- E. SPAN sessions
- F. RBAC users
Answer: CDE
Explanation: VDC resource templates set the minimum and maximum limits for shared physical device resources when you create the VDC. The Cisco NX-OS software reserves the minimum limit for the resource to the VDC. Any resources allocated to the VDC beyond the minimum are based on the maximum limit and availability on the device.
You can explicitly specify a VDC resource template, or you can use the default VDC template provided by the Cisco NX-OS software. VDC templates set limits on the following resources:
✑ IPv4 multicast route memory
✑ IPv6 multicast route memory
✑ IPv4 unicast route memory
✑ IPv6 unicast route memory
✑ Port channels
✑ Switch Port Analyzer (SPAN) sessions
✑ VLANs
✑ Virtual routing and forwarding instances (VRFs)
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/sw/nx-os/virtual_device_context/configuration/guide/b-7k-Cisco-Nexus-7000-Series-NX-OS-Virtual-Device-Context-Configuration-Guide/vdc-res-template.html
NEW QUESTION 14
What must be enabled on the interface of a multicast-enabled device to support the Source Specific Multicast feature?
- A. IGMP version 3
- B. IGMP version 2
- C. IGMP version 1
- D. PIM
Answer: A
Explanation: IGMP is the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) standards track protocol used for hosts to signal multicast group membership to routers. Version 3 of this protocol supports source filtering, which is required for SSM. To run SSM with IGMPv3, SSM must be supported in the Cisco IOS router, the host where the application is running, and the application itself. IGMP v3lite and URD are two Cisco-developed transition solutions that enable the immediate development and deployment of SSM services, without the need to wait for the availability of full IGMPv3 support in host operating systems and SSM receiver applications. IGMP v3lite is a solution for application developers that allows immediate development of SSM receiver applications switching to IGMPv3 as soon as it becomes available. URD is a solution for content providers and content aggregators that enables them to deploy receiver applications that are not yet SSM enabled (through support for IGMPv3). IGMPv3, IGMP v3lite, and URD interoperate with each other, so that both IGMP v3lite and URD can easily be used as transitional solutions toward full IGMPv3 support in hosts.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios/12_2/ip/configuration/guide/fipr_c/1cfssm.html
Topic 6, Implementing Network Virtualization in Cisco Data Center Environment
NEW QUESTION 15
Which protocol is responsible for the discovery of FCoE capabilities on a remote switch?
- A. DCE
- B. DCBx
- C. CDP
- D. LLDP
Answer: B
Explanation: Data Center Bridging Capabilities Exchange Protocol (DCBX): a discovery and capability exchange protocol that is used for conveying capabilities and configuration of the above features between neighbors to ensure consistent configuration across the network. This protocol leverages functionality provided by IEEE 802.1AB (LLDP). It is actually included in the 802.1az standard.
Reference: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_center_bridging
NEW QUESTION 16
Which two RFCs are supported by Cisco NX-OS devices for OSPFv2? (Choose two.)
- A. RFC 2238
- B. RFC 1918
- C. RFC 1583
- D. RFC 2453
- E. RFC 2740
Answer: AC
Recommend!! Get the Full 642-997 dumps in VCE and PDF From Certleader, Welcome to Download: https://www.certleader.com/642-997-dumps.html (New 151 Q&As Version)
