642-997 Exam
Tested 642-997 Free Practice Questions 2021

Act now and download your 642 997 dumps today! Do not waste time for the worthless 642 997 dumps tutorials. Download 642 997 dumps with real questions and answers and begin to learn 642 997 dumps with a classic professional.
Free demo questions for Cisco 642-997 Exam Dumps Below:
NEW QUESTION 1
What is the role of the system manager in a stateful process restart?
- A. performing software upgrades
- B. launching, stopping, monitoring, and restarting services
- C. handling message routing and queuing between services
- D. storing and managing the operational runtime information of processes
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 2
Which two statements about implementing Cisco NPV and NPIV on a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch are true? (Choose two.)
- A. STP must run inside the FP network.
- B. All VLANs must be in the same mode, CE, or FP.
- C. FP port can join the private and nonprivate VLANs.
- D. Only F and M series modules can run FabricPath.
- E. These require an enhanced Layer 2 license to run.
Answer: BE
Explanation: With the Nexus 5x00 switch, FCoE functionality is a licensed feature. After the license is installed, FCoE configuration can be completed.
Reference: http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=2030048&seqNum=4
NEW QUESTION 3
Which policy-map action performs congestion avoidance?
- A. priority
- B. bandwidth
- C. queue-limit
- D. random-detect
Answer: D
Explanation: Congestion avoidance techniques monitor network traffic loads in an effort to anticipate and avoid congestion at common network bottlenecks. Congestion avoidance is achieved through packet dropping. Among the more commonly used congestion avoidance mechanisms is Random Early Detection (RED), which is optimum for high-speed transit networks. Cisco IOS QoS includes an implementation of RED that, when configured, controls when the router drops packets. If you do not configure Weighted Random Early
Detection (WRED), the router uses the cruder default packet drop mechanism called tail drop.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios/12_2/qos/configuration/guide/fqos_c/qcfconav.ht ml
NEW QUESTION 4
Which statement about the MPLS feature set is true?
- A. It is not license dependent.
- B. It can be installed from any VDC.
- C. It can be enabled only in the default VDC.
- D. It must be installed from the default VDC.
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 5
When a local RBAC user account has the same name as a remote user account on an AAA server, what happens when a user with that name logs into a Cisco Nexus switch?
- A. The user roles from the remote AAA user account are applied, not the configured local user roles.
- B. All the roles are merged (logical OR).
- C. The user roles from the local user account are applied, not the remote AAA user roles.
- D. Only the roles that are defined on both accounts are merged (logical AND).
Answer: C
Explanation: If you have a user account configured on the local Cisco NX-OS device that
has the same name as a remote user account on an AAA server, the Cisco NX-OS software applies the user roles for the local user account to the remote user, not the user roles configured on the AAA server.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/sw/4_1/nx-os/security/configuration/guide/sec_nx-os-cfg/sec_rbac.html
NEW QUESTION 6
By default it will take 10 seconds for authentication to fail due to an unresponsive RADIUS server before a Cisco Nexus series switch reverts to another RADIUS server or local authentication. What is one efficient way to improve the reaction time to a RADIUS server failure?
- A. Decrease the global RADIUS retransmission count to 1.
- B. Decrease the global RADIUS timeout interval to 5 seconds.
- C. Configure the RADIUS retransmission count and timeout interval per server, versus globally.
- D. Configure per server a test idle timer, along with a username and password.
Answer: D
Explanation: You can monitor the availability of RADIUS servers. These parameters include the username and password to use for the server and an idle timer. The idle timer specifies the interval during which a RADIUS server receives no requests before the Nexus 5000 Series switch sends out a test packet. You can configure this option to test servers periodically. The test idle timer specifies the interval during which a RADIUS server receives no requests before the Nexus 5000 Series switch sends out a test packet. The default idle timer value is 0 minutes. When the idle time interval is 0 minutes, the Nexus 5000 Series switch does not perform periodic RADIUS server monitoring.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/nexus5000/sw/configuration/guid e/cli_rel_4_0_1a/CLIConfigurationGuide/sec_radius.html
NEW QUESTION 7
Which Cisco Nexus platform security feature provides an intelligent and scalable access control solution that mitigates security access risks across the entire network?
- A. IPsec
- B. Cisco TrustSec
- C. Management RBAC
- D. Cisco Trust Agent
- E. Cisco Secure ACS
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 8
DRAG DROP
Drag the security description on the left to the appropriate security feature on the right.
Answer:
Explanation: IP Source guard: IP Source Guard provides source IP address filtering on a Layer 2 port to prevent a malicious host from impersonating a legitimate host by assuming the legitimate host's IP address. The feature uses dynamic DHCP snooping and static IP source binding to match IP addresses to hosts on untrusted Layer 2 access ports.
Initially, all IP traffic on the protected port is blocked except for DHCP packets. After a client receives an IP address from the DHCP server, or after static IP source binding is configured by the administrator, all traffic with that IP source address is permitted from that client. Traffic from other hosts is denied. This filtering limits a host's ability to attack the network by claiming a neighbor host's IP address. IP Source Guard is a port-based feature that automatically creates an implicit port access control list (PACL).
CoPP: Control Plane Policing (CoPP) introduced the concept of early rate-limiting protocol specific traffic destined to the processor by applying QoS policies to the aggregate control- plane interface. Control Plane Protection extends this control plane functionality by providing three additional control-plane subinterfaces under the top-level (aggregate) control-plane interface. Each subinterface receives and processes a specific type of control-plane traffic.
Dynamic Arp Inspection: Dynamic ARP inspection is a security feature that validates ARP packets in a network. It intercepts, logs, and discards ARP packets with invalid IP-to- MAC address bindings. This capability protects the network from certain man-in-the-middle attacks.
Dynamic ARP inspection ensures that only valid ARP requests and responses are relayed. The switch performs these activities: Intercepts all ARP requests and responses on untrusted ports
Intercepts all ARP requests and responses on untrusted ports
• Verifies that each of these intercepted packets has a valid IP-to-MAC address binding before updating the local ARP cache or before forwarding the packet to the appropriate destination
Verifies that each of these intercepted packets has a valid IP-to-MAC address binding before updating the local ARP cache or before forwarding the packet to the appropriate destination
•Drops invalid ARP packets
Unicast RPF: The Unicast RPF feature reduces problems that are caused by the introduction of malformed or forged (spoofed) IP source addresses into a network by discarding IP packets that lack a verifiable IP source address. For example, a number of
Network (TFN) attacks, can take advantage of forged or rapidly changing source IP addresses to allow attackers to thwart efforts to locate or filter the attacks. Unicast RPF deflects attacks by forwarding only the packets that have source addresses that are valid and consistent with the IP routing table.
When you enable Unicast RPF on an interface, the device examines all ingress packets received on that interface to ensure that the source address and source interface appear in the routing table and match the interface on which the packet was received. This examination of source addresses relies on the Forwarding Information Base (FIB).
Traffic Storm Control: A traffic storm occurs when packets flood the LAN, creating excessive traffic and degrading network performance. You can use the traffic storm control feature to prevent disruptions on Layer 2 ports by a broadcast, multicast, or unicast traffic storm on physical interfaces.
Traffic storm control (also called traffic suppression) allows you to monitor the levels of the incoming broadcast, multicast, and unicast traffic over a 1-second interval. During this interval, the traffic level, which is a percentage of the total available bandwidth of the port, is compared with the traffic storm control level that you configured. When the ingress traffic reaches the traffic storm control level that is configured on the port, traffic storm control drops the traffic until the interval ends.
NEW QUESTION 9
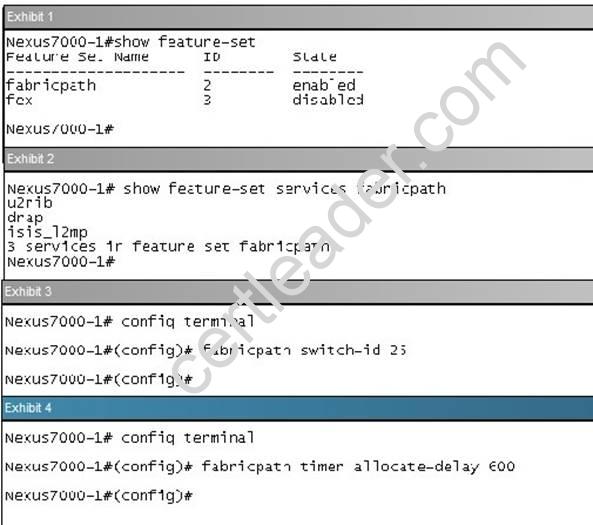
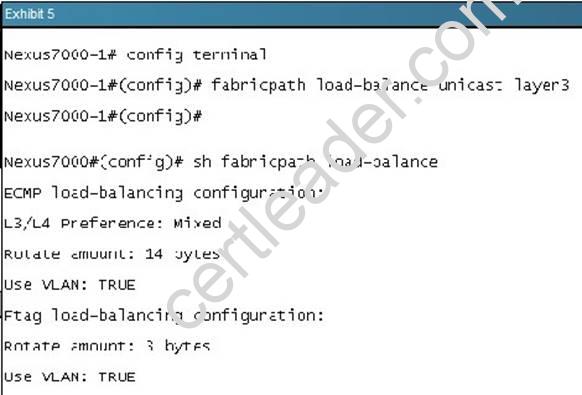
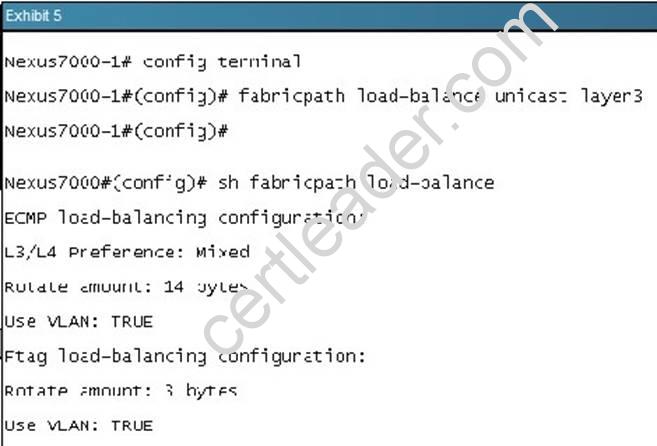
What is effect of the command “fabricpath load-balance unicast Iayer3”?
- A. It configures F2 VDC FabricPath unicast load balancing
- B. The command automatically load balances broadcast traffic
- C. It configures F1/MI VDC FabricPath unicast load balancing
- D. It configures M1 VDC FabricPath unicast load balancing
Answer: C
Explanation: The F1 cards are complemented by M1 card for routing purposes. When using M1 cards in the same virtual device context (VDC) as the F1 card, routing is offloaded to the M1 cards, and more routing capacity is added to the F1 card by putting more M1 ports into the same VDC as the F1 card.
NEW QUESTION 10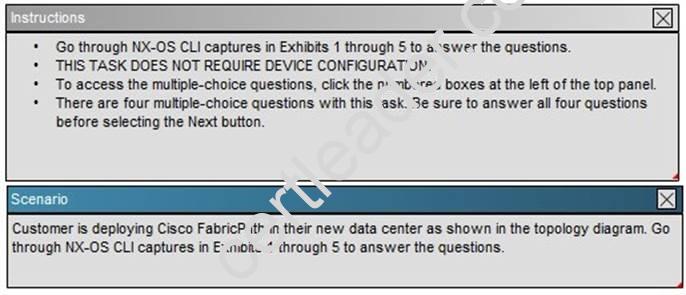
On a Cisco Nexus7000 switches what is true regarding Cisco FabricPath requirements?
- A. Ensure that you have installed the Enhanced Layer 2 license and that you have installed an F Series module
- B. Ensure that you have installed the Enhanced Layer 2 license and that you have installed an M Series module
- C. Ensure that you have installed the Enhanced Layer 3 license and that you have installed an M Series module
- D. Ensure that you have installed the Scalable Feature License license and that you have installed an F Series module
Answer: A
Explanation: FabricPath switching has the following prerequisites: You should have a working knowledge of Classical Ethernet Layer 2 functioning.
You should have a working knowledge of Classical Ethernet Layer 2 functioning.
• You must install the FabricPath feature set on the default and nondefault VDC before you enable FabricPath on the switch. See Configuring Feature Set for FabricPath for information on installing the FabricPath feature set.
You must install the FabricPath feature set on the default and nondefault VDC before you enable FabricPath on the switch. See Configuring Feature Set for FabricPath for information on installing the FabricPath feature set.
•You are logged onto the device.
•Ensure that you have installed the Enhanced Layer 2 license.
•You are in the correct virtual device context (VDC). A VDC is a logical representation of a set of system resources. You can use the switchto vdc command with a VDC number.
•You are working on the F Series module.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/datacenter/sw/5_x/nx-oQsu/feasbtriicopnaNtho/c:o3n9fig-ur(aTtoiopnic/g4u)ide/fp_switching.html
NEW QUESTION 11
Refer to the exhibit.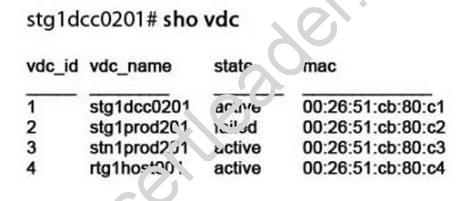
Which command would you execute to attempt a recovery?
- A. switchto vdc stg1prod201 reload
- B. reload vdc 2
- C. reload vdc stg1prod201
- D. restart vdc stg1prod201
- E. swtichto vdc stg1prod201 restart
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 12
Which two standard technologies are leveraged by Cisco DCNM to provide a web services API? (Choose two.)
- A. SSL
- B. CMD
- C. XML
- D. JAVA
- E. SOAP
Answer: CE
NEW QUESTION 13
Which statement about the Layer 3 card on the Cisco Nexus 5500 Series Switch is true?
- A. BGP support is not provided, but RIP, EIGRP, and OSPF support is provided.
- B. Up to two 4-port cards are supported with up to 160 Gb/s of Layer 3 forwarding capability.
- C. Up to 16 FEX connections are supported.
- D. Port channels cannot be configured as Layer 3 interfaces.
Answer: C
Explanation: From the Cisco NX-OS 5.1(3)N1(1) release and later releases, each Cisco Nexus 5500
Series device can manage and support up to 24 FEXs without Layer 3. With Layer 3, the number of FEXs supported per Cisco Nexus 5500 Series device is 8. With Enhanced vPC and a dual-homed FEX topology each FEX is managed by both Cisco Nexus 5000 Series devices. As a result, one pair of Cisco Nexus 5500 Series devices can support up to 24 FEXs and 16 FEXs for Layer 2 and Layer 3.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/datacenter/nexus5000/sw/mkt_ops_guides/513
_n1_1/n5k_enhanced_vpc.html
NEW QUESTION 14
Which two statements about implementing Cisco NPV and NPIV on a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch are true? (Choose two.)
- A. STP must run inside the FP network.
- B. All VLANs must be in the same mode, CE, or FP.
- C. FP port can join the private and nonprivate VLANs.
- D. Only F and M series modules can run FabricPath.
- E. These require an enhanced Layer 2 license to run.
Answer: BE
NEW QUESTION 15
Which two actions are required before FIPS is configured in Cisco MDS? (Choose two.)
- A. Passwords must be a minimum of 10 characters in length.
- B. SNMP v2 or v3 must be enabled.
- C. Remote authentication must occur utilizing RADIUS/TACACS+.
- D. Disable VRRP.
- E. Delete all SSH server RSA key pairs.
- F. Delete all IKE policies utilizing MD5 or DES for encryption.
- G. Enable the FC-FIPS feature.
- H. Disable SSH.
Answer: DF
NEW QUESTION 16
Refer to the exhibit.
What is the consequence of configuring peer-gateway on the two vPC peers N7K-1 and N7K-2?
- A. Nothing, this is the standard vPC configuration to make the feature work.
- B. The downstream device detects only one of the vPC peers as its gateway.
- C. The downstream device can use DMAC of N7K-1 on the link to N7K-2, and N7K-2 forwards the packet.
- D. This configuration enables the downstream device to use DHCP to obtain its default gateway.
Answer: C
Explanation: Beginning with Cisco NX-OS 4.2(1), you can configure vPC peer devices to act as the gateway even for packets that are destined to the vPC peer device's MAC address. Use the peer-gateway command to configure this feature.
Some network-attached storage (NAS) devices or load-balancers may have features aimed to optimize the performances of particular applications. Essentially these features avoid performing a routing-table lookup when responding to a request that originated form a host not locally attached to the same subnet. Such devices may reply to traffic using the MAC address of the sender Cisco Nexus 7000 device rather than the common HSRP gateway. Such behavior is non-complaint with some basic Ethernet RFC standards. Packets reaching a vPC device for the non-local router MAC address are sent across the peer-link and could be dropped by the built in vPC loop avoidance mechanism if the final destination is behind another vPC.
The vPC peer-gateway capability allows a vPC switch to act as the active gateway for packets that are addressed to the router MAC address of the vPC peer. This feature enables local forwarding of such packets without the need to cross the vPC peer-link. In this scenario, the feature optimizes use of the peer-link and avoids potential traffic loss. Configuring the peer-gateway feature needs to be done on both primary and secondary vPC peers and is non-disruptive to the operations of the device or to the vPC traffic. The vPC peer-gateway feature can be configured globally under the vPC domain submode. When enabling this feature it is also required to disable IP redirects on all interface VLANs mapped over a vPC VLAN to avoid generation of IP redirect messages for packets switched through the peer gateway router. When the feature is enabled in the vPC domain, the user is notified of such a requirement through an appropriate message.
Packets arriving at the peer-gateway vPC device will have their TTL decremented, so packets carrying TTL = 1 may be dropped in transit due to TTL expire. This needs to be taken into account when the peer-gateway feature is enabled and particular network protocols sourcing packets with TTL = 1 operate on a vPC VLAN.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/sw/4_2/nx-os/interfaces/configuration/guide/if_nxos/if_vPC.html
Recommend!! Get the Full 642-997 dumps in VCE and PDF From Certleader, Welcome to Download: https://www.certleader.com/642-997-dumps.html (New 151 Q&As Version)
