MCIA-Level-1 Exam
Down To Date MuleSoft Certified Integration Architect - Level 1 MCIA-Level-1 Exam Topics

It is more faster and easier to pass the MuleSoft MCIA-Level-1 exam by using Verified MuleSoft MuleSoft Certified Integration Architect - Level 1 questuins and answers. Immediate access to the Improved MCIA-Level-1 Exam and find the same core area MCIA-Level-1 questions with professionally verified answers, then PASS your exam with a high score now.
Also have MCIA-Level-1 free dumps questions for you:
NEW QUESTION 1
An integration Mute application is being designed to process orders by submitting them to a backend system for offline processing. Each order will be received by the Mute application through an HTTPS POST and must be acknowledged immediately. Once acknowledged, the order will be submitted to a backend system. Orders that cannot be successfully submitted due to rejections from the backend system will need to be processed manually (outside the backend system).
The Mule application will be deployed to a customer-hosted runtime and is able to use an existing ActiveMQ broker if needed.
The backend system has a track record of unreliability both due to minor network connectivity issues and longer outages.
What idiomatic (used for their intended purposes) combination of Mule application components and ActiveMQ queues are required to ensure automatic submission of orders to the backend system, while minimizing manual order processing?
- A. An On Error scope Non-persistent VM ActiveMQ Dead Letter Queue for manual processing
- B. An On Error scope MuleSoft Object Store ActiveMQ Dead Letter Queue for manual processing
- C. Until Successful component MuleSoft Object Store ActiveMQ is NOT needed or used
- D. Until Successful component ActiveMQ long retry Queue ActiveMQ Dead Letter Queue for manual processing
Answer: D
Explanation:
Correct answer is using below set of activities Until Successful component ActiveMQ long retry Queue ActiveMQ Dead Letter Queue for manual processing We will see why this is correct answer but before that lets understand few of the concepts which we need to know. Until Successful Scope The Until Successful scope processes messages through its processors until the entire operation succeeds. Until Successful repeatedly retries to process a message that is attempting to complete an activity such as: - Dispatching to outbound endpoints, for example, when calling a remote web service that may have availability issues. - Executing a component method, for example, when executing on a Spring bean that may depend on unreliable resources. - A sub-flow execution, to keep re-executing several actions until they all succeed, - Any other message processor execution, to allow more complex scenarios. How this will help requirement : Using Until Successful Scope we can retry sending the order to backend systems in case of error to avoid manual processing later. Retry values can be configured in Until Successful Scope Apache ActiveMQ It is an open source message broker written in Java together with a full Java Message Service client ActiveMQ has the ability to deliver messages with delays thanks to its scheduler. This functionality is the base for the broker redelivery plug-in. The redelivery plug-in can intercept dead letter processing and reschedule the failing messages for redelivery. Rather than being delivered to a DLQ, a failing message is scheduled to go to the tail of the original queue and redelivered to a message consumer. How this will help requirement : If backend application is down for a longer duration where Until Successful Scope wont work, then we can make use of ActiveMQ long retry Queue. The redelivery plug-in can intercept dead letter processing and reschedule the failing messages for redelivery. Mule Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/mule-runtime/4.3/migration-core-until-successful
NEW QUESTION 2
An integration Mule application is deployed to a customer-hosted multi-node Mule 4 runtime duster. The Mule application uses a Listener operation of a JMS connector to receive incoming messages from a JMS
queue.
How are the messages consumed by the Mule application?
- A. Depending on the JMS provider's configuration, either all messages are consumed by ONLY the primary cluster node or else ALL messages are consumed by ALL cluster nodes
- B. Regardless of the Listener operation configuration, all messages are consumed by ALL cluster nodes
- C. Depending on the Listener operation configuration, either all messages are consumed by ONLY the primary cluster node or else EACH message is consumed by ANY ONE cluster node
- D. Regardless of the Listener operation configuration, all messages are consumed by ONLY the primary cluster node
Answer: C
Explanation:
Correct answer is Depending on the Listener operation configuration, either all messages are consumed by ONLY the primary cluster node or else EACH message is consumed by ANY ONE cluster node
For applications running in clusters, you have to keep in mind the concept of primary node and how the connector will behave. When running in a cluster, the JMS listener default behavior will be to receive messages only in the primary node, no matter what kind of destination you are consuming from. In case of consuming messages from a Queue, you’ll want to change this configuration to receive messages in all the nodes of the cluster, not just the primary.
This can be done with the primaryNodeOnly parameter:
<jms:listener config-ref="config" destination="${inputQueue}" primaryNodeOnly="false"/>
NEW QUESTION 3
An organization uses a set of customer-hosted Mule runtimes that are managed using the Mulesoft-hosted control plane. What is a condition that can be alerted on from Anypoint Runtime Manager without any custom components or custom coding?
- A. When a Mule runtime on a given customer-hosted server is experiencing high memory consumption during certain periods
- B. When an SSL certificate used by one of the deployed Mule applications is about to expire
- C. When the Mute runtime license installed on a Mule runtime is about to expire
- D. When a Mule runtime's customer-hosted server is about to run out of disk space
Answer: A
Explanation:
Correct answer is When a Mule runtime on a given customer-hosted server is experiencing high memory consumption during certain periods Using Anypoint Monitoring, you can configure two different types of alerts: Basic alerts for servers and Mule apps Limit per organization: Up to 50 basic alerts for users who do not have a Titanium subscription to Anypoint Platform You can set up basic alerts to trigger email notifications when a metric you are measuring passes a specified threshold. You can create basic alerts for the following metrics for servers or Mule apps: For on-premises servers and CloudHub apps: * CPU utilization * Memory utilization * Thread count Advanced alerts for graphs in custom dashboards in Anypoint Monitoring. You must have a Titanium subscription to use this feature. Limit per organization: Up to 20 advanced alerts
NEW QUESTION 4
Mule applications need to be deployed to CloudHub so they can access on-premises database systems. These systems store sensitive and hence tightly protected data, so are not accessible over the internet.
What network architecture supports this requirement?
- A. An Anypoint VPC connected to the on-premises network using an IPsec tunnel or AWS DirectConnect, plus matching firewall rules in the VPC and on-premises network
- B. Static IP addresses for the Mule applications deployed to the CloudHub Shared Worker Cloud, plus matching firewall rules and IPwhitelisting in the on-premises network
- C. An Anypoint VPC with one Dedicated Load Balancer fronting each on-premises database system, plus matching IP whitelisting in the load balancer and firewall rules in the VPC and on-premises network
- D. Relocation of the database systems to a DMZ in the on-premises network, with Mule applications deployed to the CloudHub Shared Worker Cloud connecting only to the DMZ
Answer: A
Explanation:
* "Relocation of the database systems to a DMZ in the on-premises network, with Mule applications deployed
to the CloudHub Shared Worker Cloud connecting only to the DMZ" is not a feasible option
* "Static IP addresses for the Mule applications deployed to the CloudHub Shared Worker Cloud, plus matching firewall rules and IP whitelisting in the on-premises network" - It is risk for sensitive data. - Even if you whitelist the database IP on your app, your app wont be able to connect to the database so this is also not a feasible option
* "An Anypoint VPC with one Dedicated Load Balancer fronting each on-premises database system, plus matching IP whitelisting in the load balancer and firewall rules in the VPC and on-premises network" Adding one VPC with a DLB for each backend system also makes no sense, is way too much work. Why would you add a LB for one system.
* Correct Answer "An Anypoint VPC connected to the on-premises network using an IPsec tunnel or AWS DirectConnect, plus matching firewall rules in the VPC and on-premises network"
IPsec Tunnel You can use an IPsec tunnel with network-to-network configuration to connect your on-premises data centers to your Anypoint VPC. An IPsec VPN tunnel is generally the recommended solution for VPC to on-premises connectivity, as it provides a standardized, secure way to connect. This method also integrates well with existing IT infrastructure such as routers and appliances.
Reference: https://docs.mulesoft.com/runtime-manager/vpc-connectivity-methods-concept
Diagram Description automatically generated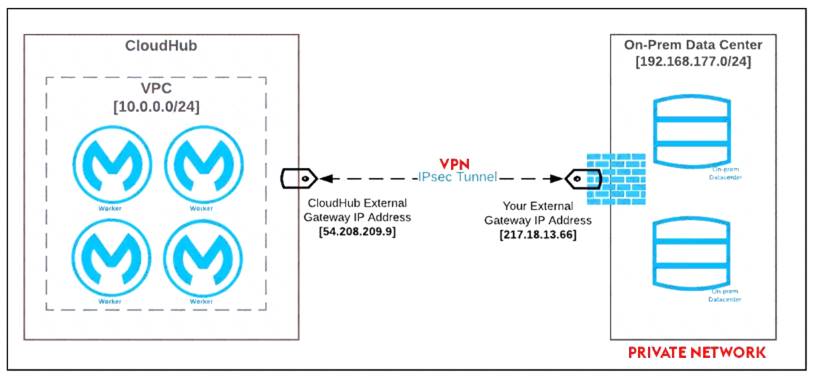
NEW QUESTION 5
An organization has strict unit test requirement that mandate every mule application must have an MUnit test suit with a test case defined for each flow and a minimum test coverage of 80%.
A developer is building Munit test suit for a newly developed mule application that sends API request to an
external rest API.
What is the effective approach for successfully executing the Munit tests of this new application while still achieving the required test coverage for the Munit tests?
- A. Invoke the external endpoint of the rest API from the mule floors
- B. Mark the rest API invocations in the Munits and then call the mocking service flow that simulates standard responses from the REST API
- C. Mock the rest API invocation in the Munits and return a mock response for those invocations
- D. Create a mocking service flow to simulate standard responses from the rest API and then configure the mule flows to call the marking service flow
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 6
As a part of design , Mule application is required call the Google Maps API to perform a distance computation. The application is deployed to cloudhub.
At the minimum what should be configured in the TLS context of the HTTP request configuration to meet these requirements?
- A. The configuration is built-in and nothing extra is required for the TLS context
- B. Request a private key from Google and create a PKCS12 file with it and add it in keyStore as a part of TLS context
- C. Download the Google public certificate from a browser, generate JKS file from it and add it in key store as a part of TLS context
- D. Download the Google public certificate from a browser, generate a JKS file from it and add it in Truststore as part of the TLS context
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 7
A Mule application currently writes to two separate SQL Server database instances across the internet using a single XA transaction. It is 58. proposed to split this one transaction into two separate non-XA transactions with no other changes to the Mule application.
What non-functional requirement can be expected to be negatively affected when implementing this change?
- A. Throughput
- B. Consistency
- C. Response time
- D. Availability
Answer: B
Explanation:
Correct answer is Consistency as XA transactions are implemented to achieve this. XA transactions are added in the implementation to achieve goal of ACID properties. In the context of transaction processing, the acronym ACID refers to the four key properties of a transaction: atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability. Atomicity : All changes to data are performed as if they are a single operation. That is, all the changes are performed, or none of them are. For example, in an application that transfers funds from one account to another, the atomicity property ensures that, if a debit is made successfully from one account, the corresponding credit is made to the other account. Consistency : Data is in a consistent state when a transaction starts and when it ends.For example, in an application that transfers funds from one account to another, the consistency property ensures that the total value of funds in both the accounts is the same at the start and end of each transaction. Isolation : The intermediate state of a transaction is invisible to other transactions. As a result, transactions that run concurrently appear to be serialized. For example, in an application that transfers funds from one account to another, the isolation property ensures that another transaction sees the transferred funds in one account or the other, but not in both, nor in neither. Durability : After a transaction successfully completes, changes to data persist and are not undone, even in the event of a system failure. For example, in an application that transfers funds from one account to another, the durability property ensures that the changes made to each account will not be reversed. MuleSoft reference: https://docs.mulesoft.com/mule-runtime/4.3/xa-transactions
NEW QUESTION 8
A company wants its users to log in to Anypoint Platform using the company's own internal user credentials. To achieve this, the company needs to integrate an external identity provider (IdP) with the company's
Anypoint Platform master organization, but SAML 2.0 CANNOT be used. Besides SAML 2.0, what single-sign-on standard can the company use to integrate the IdP with their Anypoint Platform master organization?
- A. SAML 1.0
- B. OAuth 2.0
- C. Basic Authentication
- D. OpenID Connect
Answer: D
Explanation:
As the Anypoint Platform organization administrator, you can configure identity management in Anypoint Platform to set up users for single sign-on (SSO).
Configure identity management using one of the following single sign-on standards:
1) OpenID Connect: End user identity verification by an authorization server including SSO
2) SAML 2.0: Web-based authorization including cross-domain SSO
NEW QUESTION 9
An organization is designing a mule application to support an all or nothing transaction between serval database operations and some other connectors so that they all roll back if there is a problem with any of the connectors
Besides the database connector , what other connector can be used in the transaction.
- A. VM
- B. Anypoint MQ
- C. SFTP
- D. ObjectStore
Answer: A
Explanation:
Correct answer is VM VM support Transactional Type. When an exception occur, The transaction rolls back to its original state for reprocessing. This feature is not supported by other connectors.
Here is additional information about Transaction management: Table Description automatically generated
NEW QUESTION 10
Refer to the exhibit.
A Mule application is deployed to a multi-node Mule runtime cluster. The Mule application uses the competing consumer pattern among its cluster replicas to receive JMS messages from a JMS queue. To process each received JMS message, the following steps are performed in a flow:
Step l: The JMS Correlation ID header is read from the received JMS message.
Step 2: The Mule application invokes an idempotent SOAP webservice over HTTPS, passing the JMS Correlation ID as one parameter in the SOAP request.
Step 3: The response from the SOAP webservice also returns the same JMS Correlation ID.
Step 4: The JMS Correlation ID received from the SOAP webservice is validated to be identical to the JMS Correlation ID received in Step 1.
Step 5: The Mule application creates a response JMS message, setting the JMS Correlation ID message header to the validated JMS Correlation ID and publishes that message to a response JMS queue.
Where should the Mule application store the JMS Correlation ID values received in Step 1 and Step 3 so that the validation in Step 4 can be performed, while also making the overall Mule application highly available, fault-tolerant, performant, and maintainable?
- A. Both Correlation ID values should be stored in a persistent object store
- B. Both Correlation ID values should be stored In a non-persistent object store
- C. The Correlation ID value in Step 1 should be stored in a persistent object storeThe Correlation ID value in step 3 should be stored as a Mule event variable/attribute
- D. Both Correlation ID values should be stored as Mule event variable/attribute
Answer: C
Explanation:
* If we store Correlation id value in step 1 as Mule event variables/attributes, the values will be cleared after server restart and we want system to be fault tolerant.
* The Correlation ID value in Step 1 should be stored in a persistent object store.
* We don't need to store Correlation ID value in Step 3 to persistent object store. We can store it but as we also need to make application performant. We can avoid this step of accessing persistent object store.
* Accessing persistent object stores slow down the performance as persistent object stores are by default stored in shared file systems.
* As the SOAP service is idempotent in nature. In case of any failures , using this Correlation ID saved in first step we can make call to SOAP service and validate the Correlation ID.
Top of Form
Additional Information:
* Competing Consumers
are multiple consumers that are all created to receive messages from a single
Point-to-Point Channel. When the channel delivers a message, any of the consumers could potentially receive it. The messaging system's implementation determines which consumer actually receives the message, but in effect the consumers compete with each other to be the receiver. Once a consumer receives a message, it can delegate to the rest of its application to help process the message.
Diagram Description automatically generated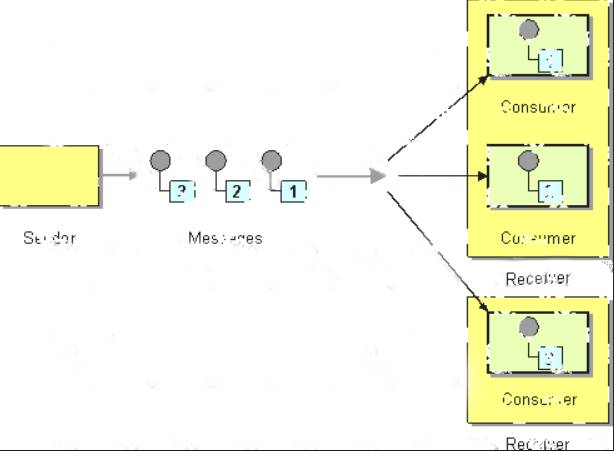
* In case you are unaware about term idempotent re is more info:
Idempotent operations means their result will always same no matter how many times these operations are invoked.
Table Description automatically generated
Bottom of Form
NEW QUESTION 11
As a part of project requirement, Java Invoke static connector in a mule 4 application needs to invoke a static method in a dependency jar file. What are two ways to add the dependency to be visible by the connectors class loader?
(Choose two answers)
- A. In the Java Invoke static connector configuration, configure a path and name of the dependency jar file
- B. Add the dependency jar file to the java classpath by setting the JVM parameters
- C. Use Maven command to include the dependency jar file when packaging the application
- D. Configure the dependency as a shared library in the project POM
- E. Update mule-artefact.json to export the Java package
Answer: BD
NEW QUESTION 12
An Order microservice and a Fulfillment microservice are being designed to communicate with their dients through message-based integration (and NOT through API invocations).
The Order microservice publishes an Order message (a kind of command message) containing the details of an order to be fulfilled. The intention is that Order messages are only consumed by one Mute application, the Fulfillment microservice.
The Fulfilment microservice consumes Order messages, fulfills the order described therein, and then publishes an OrderFulfilted message (a kind of event message). Each OrderFulfilted message can be consumed by any interested Mule application, and the Order microservice is one such Mute application.
What is the most appropriate choice of message broker(s) and message destination(s) in this scenario?
- A. Order messages are sent to an Anypoint MQ exchange OrderFulfilled messages are sent to an Anypoint MQ queue Both microservices interact with Anypoint MQ as the message broker, which must therefore scale to support the load of both microservices
- B. Order messages are sent to a JMS queu
- C. OrderFulfilled messages are sent to a JMS topic Both microservices interact with the same JMS provider (message broker) instance, which must therefore scale to support the load of both microservices
- D. Order messages are sent directly to the Fulfillment microservice
- E. OrderFulfilled messages are sent directly to the Order microservice The Order microservice interacts with one AMQP-compatible message broker and the Fulfillment microservice interacts with a different AMQP-compatible message broker, so that both message brokers can be chosen and scaled to best support the load of each microservice
- F. Order messages are sent to a JMS queu
- G. OrderFulfilled messages are sent to a JMS topic The Order microservice interacts with one JMS provider (message broker) and the Fulfillment microservice interacts with a different JMS provider, so that both message brokers can be chosen and scaled to best support the load of each microservice
Answer: B
Explanation:
* If you need to scale a JMS provider/ message broker, - add nodes to scale it horizontally or - add memory to scale it vertically * Cons of adding another JMS provider/ message broker: - adds cost. - adds complexity to use two JMS brokers - adds Operational overhead if we use two brokers, say, ActiveMQ and IBM MQ * So Two options that mention to use two brokers are not best choice. * It's mentioned that "The Fulfillment microservice consumes Order messages, fulfills the order described therein, and then publishes an OrderFulfilled message. Each OrderFulfilled message can be consumed by any interested Mule application." - When you publish a message on a topic, it goes to all the subscribers who are interested - so zero to many subscribers will receive a copy of the message. - When you send a message on a queue, it will be received by exactly one consumer. * As we need multiple consumers to consume the message below option is not valid choice: "Order messages are sent to an Anypoint MQ exchange. OrderFulfilled messages are sent to an Anypoint MQ queue. Both microservices interact with Anypoint MQ as the message broker, which must therefore scale to support the load of both microservices" * Order messages are only consumed by one Mule application, the Fulfillment microservice, so we will publish it on queue and OrderFulfilled message can be consumed by any interested Mule application so it need to be published on Topic using same broker. * Correct Answer Best choice in this scenario is: "Order messages are sent to a JMS queue. OrderFulfilled messages are sent to a JMS topic. Both microservices interact with the same JMS provider (message broker) instance, which must therefore scale to support the load of both microservices" Tried to depict scenario in diagram:
Diagram Description automatically generated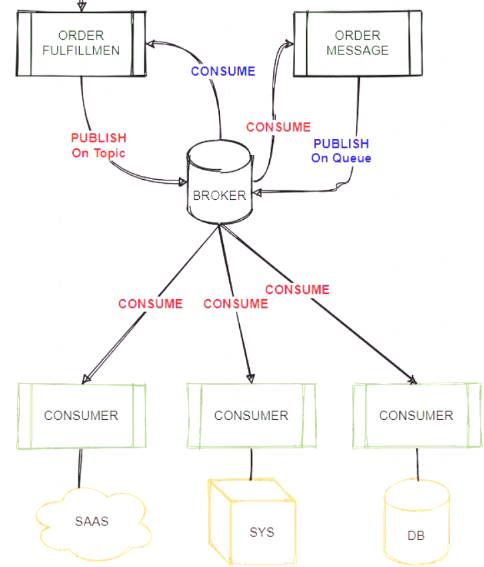
NEW QUESTION 13
A company is building an application network and has deployed four Mule APIs: one experience API, one process API, and two system APIs. The logs from all the APIs are aggregated in an external log aggregation tool. The company wants to trace messages that are exchanged between multiple API implementations. What is the most idiomatic (based on its intended use) identifier that should be used to implement Mule event tracing across the multiple API implementations?
- A. Mule event ID
- B. Mule correlation ID
- C. Client's IP address
- D. DataWeave UUID
Answer: B
Explanation:
Correct answer is Mule correlation ID By design, Correlation Ids cannot be changed within a flow in Mule 4 applications and can be set only at source. This ID is part of the Event Context and is generated as soon as the message is received by the application. When a HTTP Request is received, the request is inspected for
"X-Correlation-Id" header. If "X-Correlation-Id" header is present, HTTP connector uses this as the Correlation Id. If "X-Correlation-Id" header is NOT present, a Correlation Id is randomly generated. For Incoming HTTP Requests: In order to set a custom Correlation Id, the client invoking the HTTP request must set "X-Correlation-Id" header. This will ensure that the Mule Flow uses this Correlation Id. For Outgoing HTTP Requests: You can also propagate the existing Correlation Id to downstream APIs. By default, all outgoing HTTP Requests send "X-Correlation-Id" header. However, you can choose to set a different value to "X-Correlation-Id" header or set "Send Correlation Id" to NEVER.
NEW QUESTION 14
An API has been unit tested and is ready for integration testing. The API is governed by a Client ID Enforcement policy in all environments.
What must the testing team do before they can start integration testing the API in the Staging environment?
- A. They must access the API portal and create an API notebook using the Client ID and Client Secret supplied by the API portal in the Staging environment
- B. They must request access to the API instance in the Staging environment and obtain a Client ID and Client Secret to be used for testing the API
- C. They must be assigned as an API version owner of the API in the Staging environment
- D. They must request access to the Staging environment and obtain the Client ID and Client Secret for that environment to be used for testing the API
Answer: B
Explanation:
* It's mentioned that the API is governed by a Client ID Enforcement policy in all environments.
* Client ID Enforcement policy allows only authorized applications to access the deployed API implementation.
* Each authorized application is configured with credentials: client_id and client_secret.
* At runtime, authorized applications provide the credentials with each request to the API implementation. MuleSoft Reference: https://docs.mulesoft.com/api-manager/2.x/policy-mule3-client-id-based-policies
NEW QUESTION 15
An insurance company has an existing API which is currently used by customers. API is deployed to customer hosted Mule runtime cluster. The load balancer that is used to access any APIs on the mule cluster is only configured to point to applications hosted on the server at port 443.
Mule application team of a company attempted to deploy a second API using port 443 but the application will not start and checking logs shows an error indicating the address is already in use.
Which steps must the organization take to resolve this error and allow customers to access both the API's?
- A. Change the base path of the HTTP listener configuration in the second API to a different one from the first API
- B. Set HTTP listener configuration in both API's to allow for connections from multiple ports
- C. Move the HTTP listener configurations from the API's and package them in a mule domain project using port 443
- D. Set the HTTP listener of the second API to use different port than the one used in the first API
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 16
A Mule application name Pub uses a persistence object store. The Pub Mule application is deployed to Cloudhub and it configured to use Object Store v2.
Another Mule application name sub is being developed to retrieve values from the Pub Mule application persistence object Store and will also be deployed to cloudhub.
What is the most direct way for the Sub Mule application to retrieve values from the Pub Mule application persistence object store with the least latency?
- A. Use an object store connector configured to access the Pub Mule application persistence object store
- B. Use a VM connector configured to directly access the persistence queue of the Pub Mule application persistence object store.
- C. Use an Anypoint MQ connector configured to directly access the Pub Mule application persistence object store
- D. Use the Object store v2 REST API configured to access the Pub Mule application persistence object store.
Answer: D
Explanation:
* The Object Store V2 API enables API access to Anypoint Platform Object Store v2.
* You can configure a Mule app to use the Object Store REST API to store and retrieve values from an object store in another Mule app. However, Object Store v2 is not designed for app-to-app communication. To share data between two Mule4 apps, use a queue in Anypoint MQ.
* The Object Store v2 APIs enable you to use REST to perform the following:
- Retrieve a list of object stores and keys associated with an application.
- Store and retrieve key-value pairs in an object store.
- Delete key-value pairs from an object store.
- Retrieve Object Store usage statistics for your organization.
- Object Store provides these APIs: Object Store API
Object Store Stats API
NEW QUESTION 17
......
Recommend!! Get the Full MCIA-Level-1 dumps in VCE and PDF From 2passeasy, Welcome to Download: https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/MCIA-Level-1/ (New 273 Q&As Version)
