MCIA-Level-1 Exam
The Regenerate Guide To MCIA-Level-1 Free Download

Act now and download your MuleSoft MCIA-Level-1 test today! Do not waste time for the worthless MuleSoft MCIA-Level-1 tutorials. Download Up to the minute MuleSoft MuleSoft Certified Integration Architect - Level 1 exam with real questions and answers and begin to learn MuleSoft MCIA-Level-1 with a classic professional.
MuleSoft MCIA-Level-1 Free Dumps Questions Online, Read and Test Now.
NEW QUESTION 1
An organization has implemented the cluster with two customer hosted Mule runtimes is hosting an application.
This application has a flow with a JMS listener configured to consume messages from a queue destination. As an integration architect can you advise which JMS listener configuration must be used to receive messages in all the nodes of the cluster?
- A. Use the parameter primaryNodeOnly= "false" on the JMS listener
- B. Use the parameter primaryNodeOnly= "false" on the JMS listener with a shared subscription
- C. Use the parameter primaryNodeOnly= "true" on the JMS listener with a non•shared subscription
- D. Use the parameter primaryNodeOnly= "true" on the JMS listener
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 2
An auto mobile company want to share inventory updates with dealers Dl and D2 asynchronously and concurrently via queues Q1 and Q2. Dealer Dl must consume the message from the queue Q1 and dealer D2 to must consume a message from the queue Q2.
Dealer D1 has implemented a retry mechanism to reprocess the transaction in case of any errors while processing the inventers updates. Dealer D2 has not implemented any retry mechanism.
How should the dealers acknowledge the message to avoid message loss and minimize impact on the current implementation?
- A. Dealer D1 must use auto acknowledgement and dealer D2 can use manual acknowledgement and acknowledge the message after successful processing
- B. Dealer D1 can use auto acknowledgement and dealer D2 can use IMMEDIATE acknowledgement and acknowledge the message of successful processing
- C. Dealer D1 and dealer D2 must use AUTO acknowledgement and acknowledge the message after successful processing
- D. Dealer D1 can use AUTO acknowledgement and dealer D2 must use manual acknowledgement and acknowledge the message after successful processing
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 3
A rale limiting policy has been applied to a soap VI.2 API published in Clondhub. The API implementation catches errors in a global error handler on error propagate in the main flow for HTTP: RETRY_EXHAUSTED with HTTP status set to 429 and any with the HTTP status set to 500.
What is the expected H1TP status when the client exceeds the quota of the API calls?
- A. HTTP status 429 as defined in the HTTP:RETRY EXHAUSTED error handler in the API
- B. HTTP status 500 as defined in the ANY error handler in the API since an API:RETRY_EXHAUSTED will be generated
- C. HTTP status 401 unauthorized for policy violation
- D. HTTP status 400 from the rate-limiting policy violation since the call does not reach the back-end
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 4
Refer to the exhibit.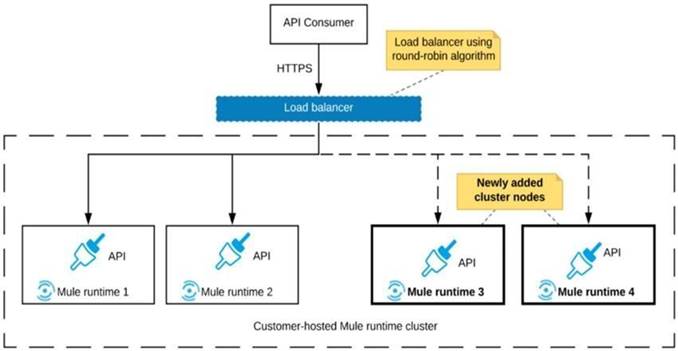
An organization uses a 2-node Mute runtime cluster to host one stateless API implementation. The API is accessed over HTTPS through a load balancer that uses round-robin for load distribution.
Two additional nodes have been added to the cluster and the load balancer has been configured to recognize the new nodes with no other change to the load balancer.
What average performance change is guaranteed to happen, assuming all cluster nodes are fully operational?
- A. 50% reduction in the response time of the API
- B. 100% increase in the throughput of the API
- C. 50% reduction In the JVM heap memory consumed by each node
- D. 50% reduction In the number of requests being received by each node
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 5
An Integration Mule application is being designed to synchronize customer data between two systems. One system is an IBM Mainframe and the other system is a Salesforce Marketing Cloud (CRM) instance. Both systems have been deployed in their typical configurations, and are to be invoked using the native protocols provided by Salesforce and IBM.
What interface technologies are the most straightforward and appropriate to use in this Mute application to interact with these systems, assuming that Anypoint Connectors exist that implement these interface technologies?
- A. IBM: DB access CRM: gRPC
- B. IBM: REST CRM:REST
- C. IBM: Active MQ CRM: REST
- D. IBM: CICS CRM: SOAP
Answer: D
Explanation:
Correct answer is IBM: CICS CRM: SOAP
* Within Anypoint Exchange, MuleSoft offers the IBM CICS connector. Anypoint Connector for IBM CICS Transaction Gateway (IBM CTG Connector) provides integration with back-end CICS apps using the CICS Transaction Gateway.
* Anypoint Connector for Salesforce Marketing Cloud (Marketing Cloud Connector) enables you to connect to the Marketing Cloud API web services (now known as the Marketing Cloud API), which is also known as the Salesforce Marketing Cloud. This connector exposes convenient operations via SOAP for exploiting the capabilities of Salesforce Marketing Cloud.
NEW QUESTION 6
What best describes the Fully Qualified Domain Names (FQDNs), also known as DNS entries, created when a Mule application is deployed to the CloudHub Shared Worker Cloud?
- A. A fixed number of FQDNs are created, IRRESPECTIVE of the environment and VPC design
- B. The FQDNs are determined by the application name chosen, IRRESPECTIVE of the region
- C. The FQDNs are determined by the application name, but can be modified by an administrator after deployment
- D. The FQDNs are determined by both the application name and the region
Answer: D
Explanation:
Every Mule application deployed to CloudHub receives a DNS entry pointing to the CloudHub. The DNS entry is a CNAME for the CloudHub Shared Load Balancer in the region to which the Mule application is deployed. When we deploy the application on CloudHub, we get a generic url to access the endpoints. Generic URL looks as below:
<application-name>.<region>.cloudhub.io <application-name> is the deployed application name which is unique across all the MuleSoft clients. <region> is the region name in which an application is deployed.
The public CloudHub (shared) load balancer already redirects these requests, where myApp is the name of the Mule application deployment to CloudHub: HTTP requests to http://myApp.
<region>.cloudhub.io redirects to
http://mule-worker-myApp.<region>.cloudhub.io:8081
HTTPS traffic to https://myApp.<region>.cloudhub.io redirects to https://mule-worker-myApp.<region>.cloudhub.io:8082
NEW QUESTION 7
An API client is implemented as a Mule application that includes an HTTP Request operation using a default configuration. The HTTP Request operation invokes an external API that follows standard HTTP status code conventions, which causes the HTTP Request operation to return a 4xx status code.
What is a possible cause of this status code response?
- A. An error occurred inside the external API implementation when processing the HTTP request that wasreceived from the outbound HTTP Request operation of the Mule application
- B. The external API reported that the API implementation has moved to a different external endpoint
- C. The HTTP response cannot be interpreted by the HTTP Request operation of the Mule application after it was received from the external API
- D. The external API reported an error with the HTTP request that was received from the outbound HTTP Request operation of the Mule application
Answer: D
Explanation:
Correct choice is: "The external API reported an error with the HTTP request that was received from the outbound HTTP Request operation of the Mule application"
Understanding HTTP 4XX Client Error Response Codes : A 4XX Error is an error that arises in cases where there is a problem with the user’s request, and not with the server.
Such cases usually arise when a user’s access to a webpage is restricted, the user misspells the URL, or when a webpage is nonexistent or removed from the public’s view.
In short, it is an error that occurs because of a mismatch between what a user is trying to access, and its availability to the user — either because the user does not have the right to access it, or because what the user is trying to access simply does not exist. Some of the examples of 4XX errors are
400 Bad Request The server could not understand the request due to invalid syntax. 401 Unauthorized Although the HTTP standard specifies "unauthorized", semantically this response means "unauthenticated". That is, the client must authenticate itself to get the requested response. 403 Forbidden The client does not have access rights to the content; that is, it is unauthorized, so the server is refusing to give the requested resource. Unlike 401, the client's identity is known to the server. 404 Not Found The server can not find the requested resource. In the browser, this means the URL is not recognized. In an API, this can also mean that the endpoint is valid but the resource itself does not exist. Servers may also send this response instead of 403 to hide the existence of a resource from an unauthorized client. This response code is probably the most famous one due to its frequent occurrence on the web. 405 Method Not Allowed The request method is known by the server but has been disabled and cannot be used. For example, an API may forbid DELETE-ing a resource. The two mandatory methods, GET and HEAD, must never be disabled and should not return this error code. 406 Not Acceptable This response is sent when the web server, after performing server-driven content negotiation, doesn't find any content that conforms to the criteria given by the user agent. The external API reported that the API implementation has moved to a different external endpoint cannot be the correct answer as in this situation 301 Moved Permanently The URL of the requested resource has been changed permanently. The new URL is given in the response.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------In Lay man's term the scenario would be: API CLIENT —> MuleSoft API - HTTP request “Hey, API.. process this” —> External API API CLIENT <– MuleSoft API - http response "I'm sorry Client.. something is wrong with that request" <– (4XX) External API
NEW QUESTION 8
An organization is designing Mule application which connects to a legacy backend. It has been reported that backend services are not highly available and experience downtime quite often. As an integration architect which of the below approach you would propose to achieve high reliability goals?
- A. Alerts can be configured in Mule runtime so that backend team can be communicated when services are down
- B. Until Successful scope can be implemented while calling backend API's
- C. On Error Continue scope to be used to call in case of error again
- D. Create a batch job with all requests being sent to backend using that job as per the availability of backend API's
Answer: B
Explanation:
Correct answer is Untill Successful scope can be implemented while calling backend API's The Until Successful scope repeatedly triggers the scope's components (including flow references) until they all succeed or until a maximum number of retries is exceeded The scope provides option to control the max number of retries and the interval between retries The scope can execute any sequence of processors that may fail for whatever reason and may succeed upon retry
NEW QUESTION 9
An organization is implementing a Quote of the Day API that caches today's quote. What scenario can use the CloudHub Object Store connector to persist the cache's state?
- A. When there is one deployment of the API implementation to CloudHub and another one to customer hosted mule runtime that must share the cache state.
- B. When there are two CloudHub deployments of the API implementation by two Anypoint Platform business groups to the same CloudHub region that must share the cache state.
- C. When there is one CloudHub deployment of the API implementation to three workers that must share the cache state.
- D. When there are three CloudHub deployments of the API implementation to three separate CloudHub regions that must share the cache state.
Answer: C
Explanation:
Object Store Connector is a Mule component that allows for simple key-value storage. Although it can serve a wide variety of use cases, it is mainly design for: - Storing synchronization information, such as watermarks. - Storing temporal information such as access tokens. - Storing user information. Additionally, Mule Runtime uses Object Stores to support some of its own components, for example: - The Cache module uses an Object Store to maintain all of the cached data. - The OAuth module (and every OAuth enabled connector) uses Object Stores to store the access and refresh tokens. Object Store data is in the same region as the worker where the app is initially deployed. For example, if you deploy to the Singapore region, the object store persists in the Singapore region. MuleSoft Reference : https://docs.mulesoft.com/object-store-connector/1.1/ Data can be shared between different instances of the Mule application. This is not recommended for Inter Mule app communication. Coming to the question, object store cannot be used to share cached data if it is deployed as separate Mule applications or deployed under separate Business Groups. Hence correct answer is When there is one CloudHub deployment of the API implementation to three workers that must share the cache state.
NEW QUESTION 10
An organization has an HTTPS-enabled Mule application named Orders API that receives requests from another Mule application named Process Orders.
The communication between these two Mule applications must be secured by TLS mutual authentication (two-way TLS).
At a minimum, what must be stored in each truststore and keystore of these two Mule applications to properly support two-way TLS between the two Mule applications while properly protecting each Mule application's keys?
- A. Orders API truststore: The Orders API public keyProcess Orders keystore: The Process Orders private key and public key
- B. Orders API truststore: The Orders API private key and public key Process Orders keystore: The Process Orders private key public key
- C. Orders API truststore: The Process Orders public keyOrders API keystore: The Orders API private key and public key Process Orders truststore: The Orders API public keyProcess Orders keystore: The Process Orders private key and public key
- D. Orders API truststore: The Process Orders public key Orders API keystore: The Orders API private key Process Orders truststore: The Orders API public key Process Orders keystore: The Process Orders private key
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 11
As a part of business requirement , old CRM system needs to be integrated using Mule application. CRM system is capable of exchanging data only via SOAP/HTTP protocol. As an integration architect who follows API led approach , what is the the below step you will perform so that you can share document with CRM team?
- A. Create RAML specification using Design Center
- B. Create SOAP API specification using Design Center
- C. Create WSDL specification using text editor
- D. Create WSDL specification using Design Center
Answer: C
Explanation:
Correct answer is Create WSDL specification using text editor SOAP services are specified using WSDL. A client program connecting to a web service can read the WSDL to determine what functions are available on the server. We can not create WSDL specification in Design Center. We need to use external text editor to create WSDL.
NEW QUESTION 12
A mule application must periodically process a large dataset which varies from 6 GB lo 8 GB from a back-end database and write transform data lo an FTPS server using a properly configured bad job scope.
The performance requirements of an application are approved to run in the cloud hub 0.2 vCore with 8 GB storage capacity and currency requirements are met.
How can the high rate of records be effectively managed in this application?
- A. Use streaming with a file storage repeatable strategy for reading records from the database and batch aggregator with streaming to write to FTPS
- B. Use streaming with an in-memory reputable store strategy for reading records from the database and batch aggregator with streaming to write to FTPS
- C. Use streaming with a file store repeatable strategy for reading records from the database and batch aggregator with an optimal size
- D. Use streaming with a file store repeatable strategy reading records from the database and batch aggregator without any required configuration
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 13
What aspects of a CI/CD pipeline for Mule applications can be automated using MuleSoft-provided Maven plugins?
- A. Compile, package, unit test, validate unit test coverage, deploy
- B. Compile, package, unit test, deploy, integration test (Incorrect)
- C. Compile, package, unit test, deploy, create associated API instances in API Manager
- D. Import from API designer, compile, package, unit test, deploy, publish to Anypoint Exchange
Answer: A
Explanation:
Correct answer is "Compile, package, unit test, validate unit test coverage, deploy"
Anypoint Platform supports continuous integration and continuous delivery using industry standard tools Mule Maven Plugin The Mule Maven plugin can automate building, packaging and deployment of Mule applications from source projects Using the Mule Maven plugin, you can automate your Mule application deployment to CloudHub, to Anypoint Runtime Fabric, or on-premises, using any of the following deployment strategies • CloudHub deployment • Runtime Fabric deployment • Runtime Manager REST API deployment • Runtime Manager agent deployment MUnit Maven Plugin The MUnit Maven plugin can automate test execution, and ties in with the Mule Maven plugin. It provides a full suite of integration and unit test capabilities, and is fully integrated with Maven and Surefire for integration with your continuous deployment environment. Since MUnit 2.x, the coverage report goal is integrated with the maven reporting section. Coverage Reports are generated during Maven’s site lifecycle, during the coverage-report goal. One of the features of MUnit Coverage is to fail the build if a certain coverage level is not reached. MUnit is not used for integration testing Also publishing to Anypoint Exchange or to create associated API instances in API Manager is not a part of CICD pipeline which can ne achieved using mulesoft provided maven plugin
Explanation
Architecture mentioned in the question can be diagrammatically put as below. Persistent Object Store is the correct answer .
* Mule Object Stores: An object store is a facility for storing objects in or across Mule applications. Mule uses object stores to persist data for eventual retrieval.
Mule provides two types of object stores:
1) In-memory store – stores objects in local Mule runtime memory. Objects are lost on shutdown of the Mule runtime. So we cant use in memory store in our scenario as we want to share watermark within all cloudhub workers
2) Persistent store – Mule persists data when an object store is explicitly configured to be persistent. Hence this watermark will be available even any of the worker goes down
Diagram Description automatically generated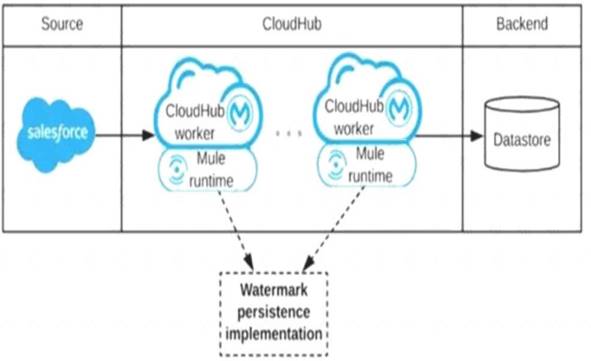
NEW QUESTION 14
Refer to the exhibit.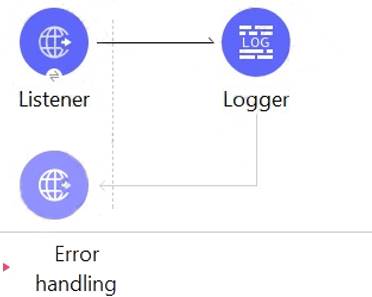
The HTTP Listener and the Logger are being handled from which thread pools respectively?
- A. CPU_INTENSIVE and Dedicated Selector pool
- B. UBER and NONBLOCKING
- C. Shared Selector Pool and CPU LITE
- D. BLOCKING _IO and UBER
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 15
Which of the below requirements prevent the usage of Anypoint MQ in a company's network? (Choose two answers)
- A. single message payload can be up to 15 MB
- B. payloads must be encrypted
- C. the message broker must be hosted on premises
- D. support for point-to-point messaging
- E. ability for a third party outside the company's network to consume events from the queue
Answer: CD
NEW QUESTION 16
Refer to the exhibit.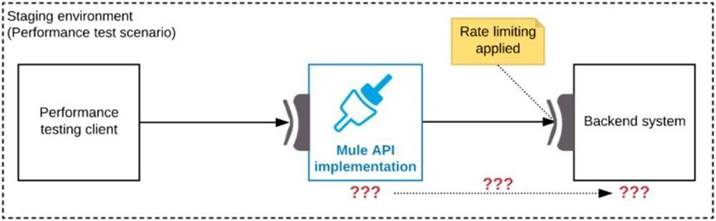
One of the backend systems invoked by an API implementation enforces rate limits on the number of requests a particular client can make. Both the backend system and the API implementation are deployed to several non-production environments in addition to production.
Rate limiting of the backend system applies to all non-production environments. The production environment, however, does NOT have any rate limiting.
What is the most effective approach to conduct performance tests of the API implementation in a staging (non-production) environment?
- A. Create a mocking service that replicates the backend system's production performance characteristics.Then configure the API implementation to use the mocking service and conduct the performance tests
- B. Use MUnit to simulate standard responses from the backend system then conduct performance tests to identify other bottlenecks in the system
- C. Include logic within the API implementation that bypasses invocations of the backend system in a performance test situatio
- D. Instead invoking local stubs that replicate typical backend system responses then conduct performance tests using this API Implementation
- E. Conduct scaled-down performance tests in the staging environment against the rate limited backend system then upscale performance results to full production scale
Answer: A
Explanation:
Correct answer is Create a mocking service that replicates the backend system’s production performance characteristics. Then configure the API implementation to use the mocking service and conduct the performance tests
* MUnit is for only Unit and integration testing for APIs and Mule apps. Not for performance Testing, even if it has the ability to Mock the backend.
* Bypassing the backend invocation defeats the whole purpose of performance testing. Hence it is not a valid answer.
* Scaled down performance tests cant be relied upon as performance of API's is not linear against load.
NEW QUESTION 17
......
Thanks for reading the newest MCIA-Level-1 exam dumps! We recommend you to try the PREMIUM Dumps-hub.com MCIA-Level-1 dumps in VCE and PDF here: https://www.dumps-hub.com/MCIA-Level-1-dumps.html (273 Q&As Dumps)
